What is an Operating System?
A program that acts as an intermediary between computer users and computer hardware
Operating System targets.
- Perform user programs and make user's problems easier to solve
- Facilitate computer systems to use
- Use computer hardware in an efficient way
Computer System Structure
The computer system can be divided into four components
Hardware - Provides Basic Computing Resources CPU, Memory, I / O Device
Operating System - Controls and coordinates the use of hardware between different applications and users
Application Program - Defines the methods in which system resources are used to solve computing
Users problems
Word processor, compiler, web browser, database system, video game
User - People, machines, other computers
Four Components of a Computer system
Operating system Definition
- OS is a resource allocation
- Manages all the resources
- Decisions between conflicting requests for efficient and appropriate resource use
- OS is a control program
- Controls the execution of programs to prevent computer errors and inappropriate use
- No universally accepted definition
- When you order an operating system, everything ships a vendor But changes wildly
- "A program that runs on the computer at all times" is the kernel. Everything else is either System programs (ships with operating systems) or application programs
- The Boot Strap program is loaded on power-up or reboot
- Usually stored in ROM or EPROM, commonly known as firmware
- Starts all aspects of the system
- Load operating system starts kernel and execution
Computer System Organization
- Computer-system operation
- One or more CPUs, device controllers connect via common bus providing access to shared memory
- Concurrent performance of CPUs and devices competing for memory cycle
Computer-System Operation
- I / O devices and CPUs can execute concurrently
- Each device controller is in charge of a particular device type
- Each device controller has a local buffer
- Captures CPU data from local memory from main memory / up to
- From the I / O device to the local buffer of the controller
- Device controller notifies the CPU that it has completed its operation because of an interrupt
Common Functions of interrupts
- Interrupt transfer control routine is usually controlled through interrupt vectors, which all service routine addresses include
- The obstructed architecture will save the address of the obstructed instructions
- The incoming blockage is disabled while another blockage is being processed to prevent an interrupted obstruction
- The trap is a software-generated interrupt that is caused by an error or user request
- An operating system is interrupted
- Operating system protects the CPU's status by registering and storing the program counter
- Determines what kind of interference has occurred
- polling
- vectored interrupt system
- Different sections of the code determine what action should be taken for each type of interference
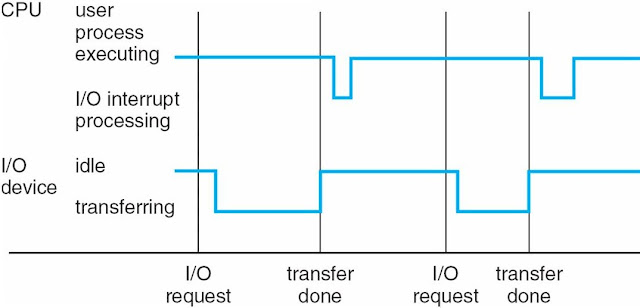
Interrupted Timeline
- System calls - requests the operating system to wait for user I / O to complete
- The device-status table contains an entry for each I / O device that reflects its type, address and status.
- The operating system indexes the I / O device table to determine the state of the device and modify the table entry. Include interruption
Direct Memory Access Structure
- Used for high-speed I / O devices that are capable of transmitting information closer to memory speed
- Device Controller transfers blocks of data from buffer storage directly into the main memory without CPU Interference
- Instead of one per bar, only one block per block is generated
Storage Structure
- Main memory - only large storage media that the CPU can access directly
- Secondary storage - Expansion of main memory which provides large non-volatile storage capacity
- Magnetic discs - Hard metal or glass platters, which are covered with the magnetic recording material
- The surface of the disc is divided logically into tracks, which are divided into sectors
- Disk controller determines logical interaction between device and computer
Storage Hierarchy
- Hierarchy storage system
- Speed
- Cost
- Instability
Caching - copying information in the fast storage system; The main memory can be seen as the final cache
Caching
- Important principles at multiple levels (hardware, operating system, software) in a computer
- Temporarily used in slow storage information temporarily
- If there is information, then fast collection (cache) was checked to determine
- If so, then information directly from the cache (faster)
- If not, the data is copied into the cache and used there
- Cache is smaller than cache storage
- Cash Management Important Design Issues
- Cash size and replacement policy
Computer System Architecture
- Most systems use a single general purpose processor (PDA through mainframe)
- Most systems also have special purpose processors
- Multiprocessor systems are increasing in usage and importance
- Also known as parallel systems, tightly-coupled systems
Clustered System
- Like a multiprocessor system, but many systems are working together
- Commonly sharing storage via the storage-area network (SAN)
- Provides a high-availability service that avoids failures
- There is a machine in the hot-standby mode in asymmetric clustering
- Symmetric clustering has several nodes, which monitor each other
- Some clusters are for high-performance computing (HPC)
- Apps must be written to use parallelization
Operating System Architecture
- Multiprogramming is needed for efficiency
- A single user can not keep CPU and I / O devices busy at all times
- Organizes multiprogramming jobs (code and data), so the CPU always has the same
- A subset of total jobs in the system is kept in memory
- One job is selected and run through job scheduling
- When it has to wait (for example I / O), OS goes to another job
- Timesharing (multitasking) is a logical extension in which CPU users are employed so often
- Interacting with each task, creating interactive computing
- Response time must be <1 second
- Each user has at least one program performed in memory [process
- f many jobs are ready to run at the same time [CPU scheduling
- If the processes do not fit in memory, swapping takes them in and out to run them.
Operating System Operation
- Handheld Powered by Hardware
- Software error or request creates exceptions or traps
- Zero division, request for operating system service
- Other process problems include infinite loops, processes that modify one or the other operating system
- The dual-mode operation allows OS to protect itself and other system components
- User mode and kernel mode
- Provided by mode bit hardware
User Transitions in Kernel Mode
- Timer to prevent endless loop/process hogging resources
- Set interrupt after a specific period
- Operating system reduction counter
- When the counter zero creates an obstacle
- Set prior to the scheduled procedure before getting the prescribed control or eliminating the program that exceeds the allotted time.
Operating System Function
Process Management
- There is a program in process execution. It is a unit of work within the system. A program is a passive unit,
- A process is an active unit.
- The process requires resources to complete its work
- CPU, memory, I / O, files
- Initial data
- The need to recover any reusable resources for the end of the process
- In the single-threaded process, there is a program counter that is to specify the location of the next instruction to execute
- Process sequentially executes instructions until it is completed at one time
- In multi-threaded process per thread is a program counter
- Usually, there are several processes in the system, some users, some operating systems are running concurrently on one or the other
- More CPU
- Consciousness by multiplying the CPU into processes/threads
Process Management Activities
- The operating system is responsible for the following activities in relation to the process Management
- Creating and deleting both user and system processes
- Suspend and resume processes
- Providing mechanisms for process synchronization
- Providing mechanisms for process communication
- Providing mechanisms to combat deadlock
Memory Management
- All data in memory before and after processing
- To perform all the instructions in memory
- Memory management determines what is in memory when
- Optimize CPU usage and computer response for users
- Memory management activities
- Keep in mind, which parts of memory are currently being used and by whom it is being done
- Decide which process (or its parts) and data to move to memory
- Allocating and Dealing Memory Space as needed
- OS provides a similar, logical approach to information storage
- Logical storage unit physical properties - file
- Each medium is controlled by the device (i.e., disk drive, tape drive)
- Different properties include speed, capacity, data transfer rate, access method (sequential or). Random)
- File system management
- Files are usually organized in directories
- Access control on most systems to determine who can access
- OS activities are included
- Creating and deleting files and directories
- Primitives to manipulate files and diaries
- Mapping files on secondary storage
- Backup files on static (non-volatile) storage media
Mass Storage Management
- Usually, the disk is used to store data that does not fit in main memory or data that should be kept for "long" The period of time
- Proper management is of central importance
- The full speed of computer operation lies on the disk subsystem and its algorithm
- MASS STORAGE ACTIVITIES
- Free space management
- Storage allocation
- Disk scheduling
- Some storage is not fast enough
- Tertiary storage includes optical storage, magnetic tape
- Still needs to be managed
- The change between WORM (writing-once, read multiple times) and RW (read-write)
Performance of Various Stages of Storage
Migration in the Register from the Disk of Integer A
- The multitasking environment should be careful to use the most recent value, no matter where it is stored in Storage hierarchy
- Multiprocessor environment should provide cache compatibility in hardware such as all CPUs The most recent value in their cache
- The situation of a distributed environment is even more complex
- Many copies of datum may be present
I / O Subsystem
- One purpose of the OS is to hide the specificity of hardware devices from the user
- The I / O subsystem is responsible for
- Memory management of I / O including buffering (data is being temporarily stored while it is being transferred), Caching (storing parts of data in fast storage for display), spooling (overlapping of output) A job with the input of other jobs)
- Common Device-Driver Interface
- Drivers for specific hardware devices


.png)
























No comments:
Post a Comment