Showing posts with label Networking. Show all posts
Showing posts with label Networking. Show all posts
Monday, 29 April 2019
Labels:
Networking,
Tech
 Hi'i'm Rahim Ansari ,from India, I Love to Blogging, Desing Website, Web Developing and Desiging I Like to Learn and share Technical Hacking/Security tips with you,I Love my Friends.
Hi'i'm Rahim Ansari ,from India, I Love to Blogging, Desing Website, Web Developing and Desiging I Like to Learn and share Technical Hacking/Security tips with you,I Love my Friends.
Friday, 25 January 2019
Labels:
Networking
 Hi'i'm Rahim Ansari ,from India, I Love to Blogging, Desing Website, Web Developing and Desiging I Like to Learn and share Technical Hacking/Security tips with you,I Love my Friends.
Hi'i'm Rahim Ansari ,from India, I Love to Blogging, Desing Website, Web Developing and Desiging I Like to Learn and share Technical Hacking/Security tips with you,I Love my Friends.
Sunday, 30 December 2018
What is Wireless Networks?
When you talk about Wireless Networks, do you feel like a complete dummy? Would you like to know more about Wireless Technology? Thinking about buying a wireless router? But where do you have a clue to start? Here's a quick and easy way to learn about wireless technology. I will now make a prediction: I think, within a decade, wireless access will make everyone's life much easier, and they will not even notice there.
What is Wireless Networking?
Wireless Networking just looks like this - a way to create networks without any wires! If this sounds exciting to you, then read on. With a wireless network, you can create a radio connection between computers that allow them to communicate and connect to the Internet, to get into all the trouble without adding them to the wires. The computer does not require a clear path to signal, because the wireless signal can be easily accessible through the walls and between the floor.
Wireless Network at Home
When most people talk about wireless networks, they are talking about wireless LAN (local area network). A local area network does not mean that it covers your entire neighborhood - the 'local area' in the question can only be a building, such as your house. So if you want wireless networking in your home, then you want a wireless LAN.
Once the people are wireless in their house, they always feel like someone has done the ultimate miracle. After years of holes in the walls and running the stars everywhere, it is really amazing to see them suddenly gone.
Wireless Networks not only at Home
It was to the home users who were the fastest to adopt the wireless technology, finally ready to pay any amount to run the stars in their house. Since then, however, the technology has started spreading in all types of offices, universities and other places.
Coffee shops and cafe chains have found that if they offer wireless internet access, their customers will stay for hours and it is also common in hotels and airports. This means that once you set up a laptop for wireless, it becomes much more portable than before.
How Wireless Networks Work
Wireless Networks work by using radio waves instead of stars to transmit data between computers. This is a simple version. If you are curious to know what is going on in more detail, then all this is explained in this article. Ones and Zeros
I'm sure you know that computers transmit data digitally using binary: people and zeros. It is a way of communication that translates very well into radio waves because a computer can transmit people and zero to different types of beeps. These beeps are so fast that they are beyond the limits of human listening - radio waves which you can not hear, in fact, all the time around you, However, using them does not have to stop the computer.
What is Morse Code in Wireless Networks
The way it works, it's like Morse Code. You probably already know that Morse code is a way of representing the alphabet so that it can be broadcasted on the radio using dot (short beep) and dash (long dash). It was used manually for years, and with the invention of the telegraph, it became a great way to get information from one place to another. This is more important for example, however, it is a binary system, exactly like the computer's zero and zero.
You can think of Wireless Networking, then, like Morse code for computers. You plug a combined radio receiver and transmitter, and the computer is capable of sending your data from one place to another, with the dots and dashes (a bit in the computer).
Wireless Networks Frequencies
You may be surprised, however, the computer may send enough bits to send and receive data at that speed. After all, there should be a limit on how much can be sent in a second, before it becomes useless, okay? Okay, yes, but the key to wireless networking is that it gets around this problem.
First of all, wireless transmissions are sent at very high frequencies, which means that more data can be sent per second. Most wireless connections use an instance of 2.4 GHz (2.4 billion cycles per second) - the same frequency for mobile phones and microwave ovens. As you know, however, this frequency of this frequency means that the wavelength should be very low, this is the reason why wireless networking Works only in a limited area.
In addition, Wireless Networks use a technique known as 'frequency hopping'. They use dozens of frequencies in the given range and switch between them continuously. This makes wireless network more immune to interfering with other radio signals if they transmit only at a frequency.
What is Access Points?
The last step is when the internet is used on all computers accessing the network. This is done using a special tool, which is called Access Point. Access points are more expensive as compared to the wireless card for a computer because they have a radio that is able to talk to about 100 computers at the same time and share access to the Internet between them. Dedicated access points are really necessary only for large networks, however - if you have only a few computers, it is possible to use one of them as an access point, or you can simply get a wireless router.
They Understand Each Other
It's all right and good, but how do the wireless devices created by different companies manage to work together when all this is so complicated? Well, the answer is that there are standards that follow all the wireless devices. These standards are technically called the 802.11 standards and are determined by IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers). Thanks to people sticking to their standards that using wireless networking today is so easy and cheap
You do not Need to Worry
If all these things in frequencies are a bit worrisome to you, then you do not have to happen - wireless networking hardware and software handles it all automatically, without needing to do anything. Do not think that you are going to tell a wireless device that another is using what frequency, because it is not just going to be okay? Wireless networking is much simpler than it is actually used for all its complex functions, which you expect.
5 Reasons why you need a Wireless Network
As far as I am concerned, the wireless network is one of the best inventions in history - they are really the best thing since the chopped bread. I mean, in fact, the bread is quite easy to bite yourself, but have you ever tried to wire the network? Therefore, in the spirit of spreading the word, I am going to tell you five reasons why you need a wireless network.
Share Internet Access
Wireless Networking gives you a cheap and easy way to share an internet connection between many computers, eliminating the need for more than one modem. You can also add new computers to your network by plugging it into a wireless card and switching on them - they get the internet connection directly! There are not many wired networks that can say this.
Share Files and Printers
A Wireless Network provides access to your files wherever you are at your home, and makes it easy to synchronize data on a laptop with a home computer. Sending files between computers with wireless networks is as easy as sending them by email, or even burning them in the CD. Also, when connected to a printer, you can write things where you want,
Press print, and go and gather them by connecting them from one printer to the other - printers that are plugged into one of the computers on the network, are automatically shared between all computers.
Play the Game
You must have seen an option to play on LAN in your favorite game. Well, wireless networks are LAN, which means that your whole family can play that game together - without the need to have computers without each other
It is far more fun to play against real people who you know to play against random people on the Internet, not to mention that the game will work very fast. You can invite your friends to bring your computer and join it - a 'LAN party'!
An added advantage is that wireless equipment lets you connect any game easily, which you or your children can do on the Internet, and start playing online. Playing online with wireless connected Xbox or PlayStation 2 is very easy, every time to connect it to your modem always on.
One major factor in the spread of broadband was that it allows the internet connection to be always on-the-go, without the need to dial. OK, wireless networking lets you keep the network connection on forever, which means that anytime your computer can connect to the Internet. Wish! You can take the laptop from the room to the room, and it does not matter - they will always have access. Also, there is no need to set up a username and password system, because the wireless networks work without logging in. It's just so convenient!
No More Virus
This, of course, is the biggest reason why you should switch your network to wireless. Wires are inconvenient, expensive, unattractive and dangerous - you will be happy to see their backs.
The average Ethernet wire does not exceed the price per meter, but once you have bought enough meters to do whatever you need to do, well, it quickly adds it. Not only this but if you want to run your strings between rooms or floors, then you will have to pierce the walls - which you are not allowed to rent. I know a lot of people in the rental apartment, who had to keep their network limited to one room until they went wireless. With wireless networking, well, you can take your computer out too, if you want!
No more stars mean the entire floor and corners. This not only improves the security of your home because it is very easy to travel on all exposed stars, but it also means that you need to go through all the hassles of packing all the stars and connecting them again. No, when you walk than the other end. It also means that if your Internet connection breaks you do not need to check every wire for damage.
Convinced
If you're excited, then it's great - keep reading these articles for advice on how to set everything up. If you do not think this is for you yet, then it is okay, do not give up on it - I am sure you will get around when you realize that it is really easy and cheap.
Yet confused Wireless Networks
Wireless Networking, like a lot of things in life - and especially what is to do with the computer - is full of jargon. Although it cannot be intimidated: talk to an English guide to help talk to a quick computer here. 802.11 The name of the wireless networking standard as determined by IEEE Ensures that wireless devices are interoperable.
Driver: A piece of computer software that tells the computer how to talk
Devices that are plugged in. For wireless networking, the drivers that you need to install will come to the CD with any of the devices you buy.
Ethernet. The most common way to connect to LAN is. Any wires that you connect your computer together now have ethernet wires, and your cable connecting your modem to your computer is probably also an ethernet wire.
Ghz Gigahertz Measurement of frequency - One gigahertz is one billion cycles per second. You can identify the measurement at the speed of the computer processor, which is now also measured in Ghz.IEEE. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers In charge of the wireless networking standard, as well as many other computer-related standards (including Ethernet standards). They ensure that computer equipment created by different manufacturers can work together.
Inter-operated This means that two pieces of equipment are compatible - you can use them together because they stick to the standards. You should not get any wireless equipment that is not interoperable.
LAN: Local Area Network A network that is usually limited to a building, such as home or office. A wireless LAN is also known as WLAN. Linux An optional operating system for Windows Computers running Linux can run many programs and can connect to the Internet without the need for Windows. Linux is free to download and you have permission to give it to friends to use. Many wireless devices run Linux or are compatible with it.
MAN: Metropolitan Area Network A network that covers a large area, for example, a city or city. Wireless MAN (men?) Spread the Internet over the entire area, but are expensive to install. They are sometimes used in university campuses. Mbps Megabits per second, a measure of the speed of the connection. Not to be confused with Mbps, megabytes per second. One megabyte consists of eight megabits.
PAN: Personal Area Network These are networks made of devices connected together in a small area. For example, your computer connected to a USB keyboard and mouse is a pan. Pan-wireless can be used using a technique called blue-tooth.
PCI: Peripheral Component Interconnect This is a way to install new devices inside your computers, such as graphics cards and network devices. If you want to install a wireless card inside your computer, then you will use the PCI.
PCMCIA: The Personal Computer Memory Card International Association (some say that it should be called 'for the People Cantored Memorized Computer Industry') is a standard for plugging credit card size devices into a laptop, to give it extra capacity.
PCMCIA is a great way to add wireless networking to your laptop as easily as inserting a disc.
USB: Universal Serial Bus A port is used to connect all types of devices to computers, including keyboards, rats, printers, external drives, and almost anything you can think of. If you do not want to open your computer and you do not have a laptop, you can get a USB wireless device.
VAN: Wide Area Network A network that is linked to more than one physical site, such as a business that has two computers connected to a network. The internet, for example, is a wan - the largest van in the world.
WEP: Wired Equivalent Privacy The old standard for encrypting wireless networks. Unfortunately, it was found unsafe back in 2001, and therefore it should not be used anymore.
WPA: Wi-Fi Protected Access Basically upgrade to WEP to fix its security
See: What is HTTP or HTTPS?
See: What is TCP/IP and How TCP/IP Works?
Labels:
Networking
 Hi'i'm Rahim Ansari ,from India, I Love to Blogging, Desing Website, Web Developing and Desiging I Like to Learn and share Technical Hacking/Security tips with you,I Love my Friends.
Hi'i'm Rahim Ansari ,from India, I Love to Blogging, Desing Website, Web Developing and Desiging I Like to Learn and share Technical Hacking/Security tips with you,I Love my Friends.
Monday, 17 December 2018
What is TCP/IP and How TCP/IP Works?
What is TCP /IP? (Transmission Control Protocol)
Overview of TCP / IP
An open network architecture that supports routing and controlled transmission on global and local networks
- Supported by almost all computer vendors
- Continuous development of TCP / IP standard
- Important Technology for the Internet
TCP / IP is also used on both global networks, such as the Internet and local area networks.
TCP / IP is an open communication architecture which is widely spread. Implementation of TCP / IP for most common types of computers.
TCP / IP was developed to connect hosts on ARPANET, which was the first implementation of the Internet. ARPANET has retired, but TCP / IP continues and is constantly being developed with new standards.
TCP / IP is currently used on the Internet where it is used as a major technology. Popular protocols in the TCP / IP family are SMTP, which is a simple Mail Transfer Protocol, FTP, for File Transfer Protocol and Telnet Protocol, which is used for remote access.
History of TCP / IP
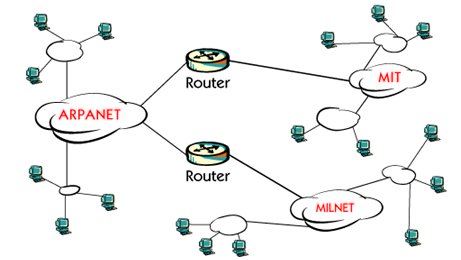
The TCP / IP United States detects its origins for a research project funded by DARPA, which is for the Defense Advanced Research Project Agency. As a result of this project, in 1969 an experimental network called ARPANET was formed. In 1975, ARPANET was put into operation, the experiment proved to be successful after it was successful. The protocol used was called NCP, which stood for the Network Control Protocol.
In 1979, the development of a new protocol suite called TCP / IP started. Many thoughts came from the NCP in the TCP / IP protocol.
In 1983, the new protocol called TCP / IP was adopted as a suite standard, and all the hosts on ARPANET needed to use it.
In 1984, ARPANET was divided into separate networks and the word was used instead of ARPANET.
In 1987, the internet was spread all over the world.
Today Internet Protocol is hindered for future development. A new version of Internet Protocol is called IPv6, which stands for IP version 6, is now standardized. This will provide great address space and support for quality of service multimedia applications.
Internet
DARPA started its work around 1969. DARPA was well-known for its ideas about secure packet-switched networks, and the result was famous ARPANET in 1975.
Many researchers involved in ARPANET. 1979 DARPA created a committee called Internet Control and Configuration Board, ICCB, which later became the Internet Architectural Board, IAB. In 1983, ARPANET was divided into two separate networks, one for research and one for military use.
The research network was still called ARPANET and the military part was called MILINET. At this time TCP / IP architecture was established and used. Also, the router technology was developed and used to isolate it individually
Network
Later in the United States, several high schools and universities were connected to this network. One example was the MIT, Massachusetts Institute of Technology. It was the beginning of the Internet.
Internet Standard
To handle all the standards required for TCP / IP architecture and Internet communication, the standardization organization was required.
As an umbrella organization for standardization, ISOC is for the Internet Society. The IAB is below the Internet Architectural Board, ISOC. IAB consists of 16 members of various companies or service providers. IAB is responsible for making standard proposals in official standards. Standard proposals are called RFCs, which means
Request for Comments. Today there are around 2200 different RFCs. Some of them are only for historical use, some are for experimental use and some are for official use.
There are three famous groups under IAB.
First, IETF is the Internet Engineering Task Force, which includes various executive groups who test all protocols before getting the final standard status by IAB.
The second is IANA, the Internet Assignment Number Authority, which is responsible for an RFC document called Assign Number. This RFC specifies different numbers for different protocols used in data communication.
The third is an IRTF, the Internet Research Task Force, which includes various research groups looking into the future; What is going to happen with the Internet and TCP / IP architecture?
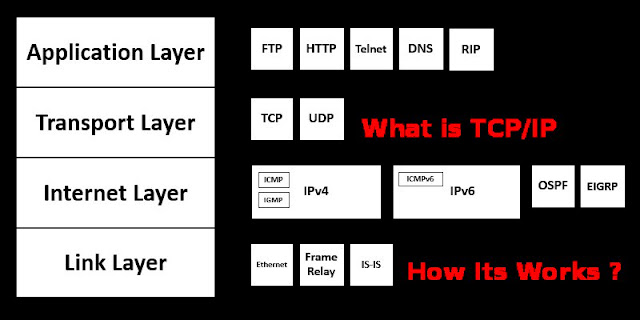
TCP / IP Family Architecture and Protocol
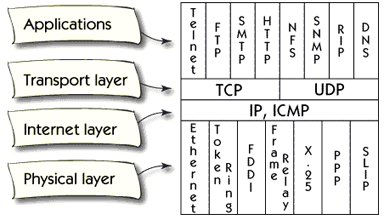
TCP / IP architecture includes only four layers.
There is a correspondence between the OSI model and layers in TCP / IP.
Layer One and Two which are physical and data link layers in the OSI model correspond to the physical layer of TCP / IP.
The network layer in the OSI model which is the layer three corresponds to the Internet layer of TCP/IP
The layer four is called the transport layer in both models.
Layer five, six and seven in the OSI model are included in the application layer of all TCP / IP architecture.
The physical layer describes the interface for different types of networks, such as Ethernet, Token Ring, and X25.
Internet layer describes Internet Protocol or IP. Internet Control Message Protocol, ICMP, is a support protocol for IP. It is used to send feedback information on the IP protocol, for example, if something goes wrong.
Transport layer describes two protocols; Transmission Control Protocol, TCP and User Datagram Protocol, UDP. Both of these protocols take the data to the correct session, but TCP does it in a reliable manner, and the UDP is unreliable.
The application layer contains hundreds of application protocols. Telnet, FTP, SMTP, and HTTP are the most common.
Traffic Flow
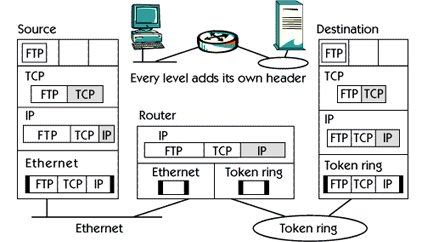
In the picture, you see a file transfer session between the source and destination host. The source host adds some extra header information to each layer. The destination host reduces this header information if everything is received properly.
In the FTP Data Transport Layer, the Transport Protocol, TCP is sent from the File Transfer application in the source host. TCP adds your header information including source and destination port number. Port number is used to separate separate sessions from each other.
Next, the data is sent to the Internet layer. IP protocol adds your header with IP address. Then everything is put in an Ethernet frame, which is sent to the router with the help of a physical address.
The router looks at the physical destination address and sees that this frame itself was addressed. If the checksum contained in the header is correct, the router sends information to the Internet layer and IP protocol.
The router uses the IP destination address and its routing table for further routing processing. In this case, the destination host is on the token ring network.
The router uses the physical address to reach the destination host. Anything sent from the router to the token ring network is taken by the destination host. If the checksum is correct, then this information is transferred to the IP protocol on the Internet layer.
The IP protocol appears in the Datagram and IP destination addresses. If this address is correct then the data is sent to the transport layer above. The TCP protocol looks at the port number in the TCP header and sees that it is FTP data. This data reaches the FTP application on the destination host.
Internet Protocol (IP)
The most important protocol in the TCP / IP family is called Internet Protocol, IP.
The IP protocol defines the structure of data packets, called datagrams.
IP is responsible for logical addresses, which are called IP addresses, and to carry data between the physical and transport layer.
The IP protocol provides a Datagram delivery service between different physical networks where TCP / IP is used. In the TCP / IP network, the router uses the IP protocol to distribute the datagram to the correct destination.
Functions of Internet Protocol (IP)
The main functions of the IP protocol are addresses, routing, and fragmentation.
The IP protocol handles routing with the help of a unique 32-bit IP address. Every host associated with the network has a unique IP address.
Fragmentation is required when two networks want to communicate with each other, but they use different packet sizes. The IP protocol needs to split the packet into smaller datagrams.
The IP protocol is a connectionless protocol, which means that it does not offer a receipt, error checking, and re-transmission. This means that if this physical layer is not controlled by the protocol, then it should be handled by the transport layer.
IP Header
To make the protocol work appropriately, a header is an additional information that should be included in the frame or datagram.
The IP protocols have different functions. It is most important to add logical IP addresses to both source and destination host. This is required for routing.
Other things included in the IP header are:
1. The version number of the IP protocol. The most commonly used version of today is 4, and the next generation IP is called version 6.
2. The IP header also has two fields with length information. IHL, which stands for the length of the internetwork header, specifies how much time a header is and where the data starts from.
3. The total length specifies the number of bytes of both the header and the data.
4. The type of service, TOS, is an area which is usually not used in the IP header.
5. Fragmentation information always starts with a zero, after which two flags are DF, which does not stand for the fragment, and the MF stands for more pieces. If the pieces are then the DF flag will be zero whereas MF will be one.
Fragment offset specifies the necessary information to the destination host to gather pieces in the correct information. It works like this. The destination host has a buffer for different pieces. Fragment offset specifies that the current section starts in the buffer. With the help of total length and IHL, this header is the length, the length of the destination host data segment can be calculated. Destination in this way
The hosts will re-assemble the pieces.
What about the identity field? The objective of the field of identification is to show which pieces are together. The pieces that are simultaneously have identical identification numbers.
6. Live to time, or TTL field is a number that explains how many routers are allowed to pass before dumping the datagram. This is necessary in order to prevent datagram from looping in the network forever. The maximum number that can be set to 255. Each router passing through datagram has reduced this number from 1.
7. Protocol field specifies the protocol on the upper layer, for example, TCP or UDP may be.
8. Header checksum is used to ensure that the contents of the IP header are not corrupted.
9. An IP address is included in two field headers. Another source for the host hosts another destination.
10. Options fields are not commonly used. Sometimes the option is used to specify options through the network
How TCP Work
TCP, which stands for Transmission Control Protocol, is one of two transport protocols in the TCP / IP family. The second is the UDP.
There are two main functions in TCP. Transfer data between the first two hosts in a reliable way. The second task is to distribute data to the right session or the application located on layers above TCP.
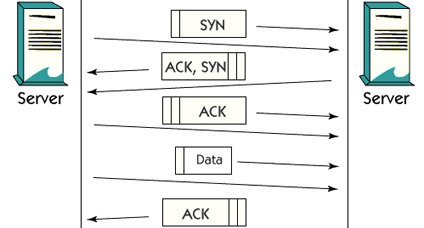
1. TCP creates a reliable service on top of Internet Protocol. This is done with the help of three-way handshaking. The source sends a sync signal. The destination sends an approval for that signal and its synchronization signal. The source accepts that signal. The connection is now established and the data can be transferred reliably. Since TCP works in this fashion, it is called a connection-oriented protocol.
2. A port number and the IP address is used to get a unique connection between two hosts. If different sessions are coming from the same host, different port numbers are used to separate these sessions.
TCP Connection
There is a three-way handshake in a TCP connection before transferring data between two hosts.
The first synchronization flag, called SYN, is sent from the source host to the destination. An ACK stands for acceptance, and a new SEN flag is returned back. It should also be confirmed by the source through the ACK. Now the connection is established and data transfer may start.
All data transferred is sent together with the serial number. This number is used to restore the data in the correct order, but there is also a checksum function, which shows how many bytes of data are transferred. The data transferred should be confirmed with the ACK by the destination host.
TCP Numbering
The synchronization signal sent by the source host contains a synchronization flag SYN, but it also contains a sequence number that provides the destination host with a reference point to access the data.
The destination host sends a signal that has four different items. The first is an ACK flag and the other is a SEN flag. The third item is the sequence number that gives the source host a reference point for the data coming from the destination host. A fourth item is a receipt number which is the sequence number that the source host should use next time. The reason for this is to ensure that communication is appropriate and
Reliable
The source host sends an approval signal that contains three separate items. The first is an ACK flag and the second is the original serial number, increased by 1. A third item is a receipt number which is the sequence number that the destination host should use next time.
Now the source host sends your data with the sequence number. This number has increased by the number of bytes transferred to the previous sequence number. The destination host accepts it by sending a signal that has three separate items. First ACK flag, next sequence number and finally an acknowledgment
Number.
Accept TCP (ACK)
A host that sends information to another host always saves a copy of the data sent.
When a receipt is received then the copy of the data is cleared, but if something goes wrong, then the copy of the data is reproduced.
TCP Windows
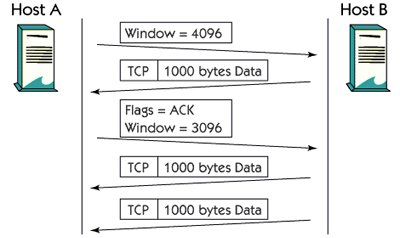
Curved shapes are used for flow control. This specifies how many additional bytes the destination host is ready to accept. This function is used when the app is not able to handle all the received data on the above layer.
In the photo, Host A sets a buffer of 4096 bytes for incoming packets. Host B sends 1000 bytes to data. A buffer at Host A is full of 1000 bytes and the window size decreases to 3096 bytes.
Many continuous packets can be sent without the need for acceptance. The only important thing is that B does not handle more data than buffer on host A.
TCP Application Ports
Port numbers are used to separate separate sessions from each other.
There are two types of ports, server ports, and customer ports. Server port is a number between 1 and 1023. The client port is a random number between 1024 and 65535.
For the widely used services, such as Telnet and FTP, these numbers have to be centrally administered. It is regulated in an RFC standard document. This RFC is 1700, whose title is the assigned number. This RFC tells other things as well as the port number assigned to the famous services.
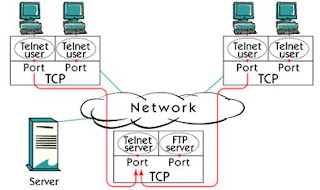
A server can handle multiple sessions at the same time. Identify a unique session between client and server's port number, source and destination host, with the IP address of the client and the server.
For example, many Telnet sessions in the picture are handled by a single host. All sessions are using the same server port number, 23, which is the server port for Telnet. TCP is capable of separating those connections from one another because they all come from different customer ports.
Functions of UDP (User Datagrame Protocol)
TCP is not the only transport protocol in the TCP / IP family. Actually, there are two. The second is the UDP, which is for User Datagram Protocol.
UDP is not capable of handling handshaking. This means that the UDP is a connectionless protocol.
The reliability should be provided by the application rather than the transport protocol.
Like TCP, UDP allows remote machines to contact a service on a certain port, but this connection does not establish. Instead, you can use it to send single packets to the destination service. It is perfect for broadcasting traffic, where all the hosts on the network are addressed to traffic.
UDP Application Ports
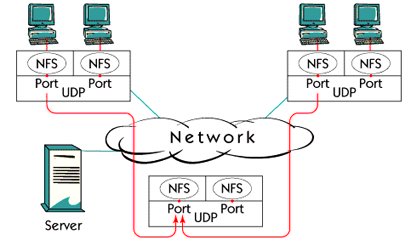
Application port in UDP works in the same way as in TCP. With the IP address of the client and the server, the client and the server's port number identify a unique session between the source and the destination host.
Port number is used to send the correct number of data. There are many types of applications using UDP. Some examples are NFS (Network File System), SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) and DNS (Domain Name Service).
See: How to Google?
See: How to Become a Computer Expert?
Labels:
Networking
 Hi'i'm Rahim Ansari ,from India, I Love to Blogging, Desing Website, Web Developing and Desiging I Like to Learn and share Technical Hacking/Security tips with you,I Love my Friends.
Hi'i'm Rahim Ansari ,from India, I Love to Blogging, Desing Website, Web Developing and Desiging I Like to Learn and share Technical Hacking/Security tips with you,I Love my Friends.
What is LAN? (Local Area Network)
History of LAN (Local Area Network)
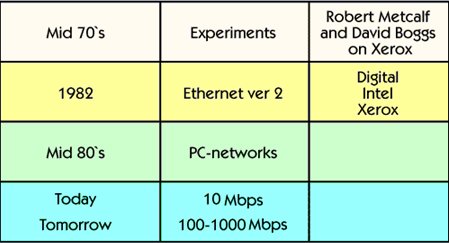
In the mid-'70s, Robert Metcalfe and Xerox used David Boggs with communication Between computers, This became the first implementation of Ethernet.
In 1982, the second edition of Ethernet was implemented by Digital, Intel, and Xerox. This is The version of Ethernet that is still in use.
In the mid-'80s, the first PC-networks were visible. Such as network components Bridges and routers were now available on the market.
The local bandwidth of the local area network is 10 Mbps today.
Topology
The network's topology deals with the physical configuration of devices and cables
Which connects them.
There are three Topologies are used for Local Area Networks(LAN):
1. Bus network: All connected hosts are just sharing the same cable on the network. All hosts should be used
The same communication speed and "listen" all the traffic on each host cable.
2. Ring Network: All hosts in the ring topology are connected in a ring. Each host receives all the data in the ring
If there is any other destination information for the data, then the host will re-send the data.
The data will continue to travel as long as the destination does not reach the destination host.
3. Star Network: A star configuration consists of a central controller that can be a hub or switch. Each host is directly connected to a port on the central controller.
Transmission Media
The IEEE standard for LAN describes various types of transmission media. It can be cable, fiber or wireless.
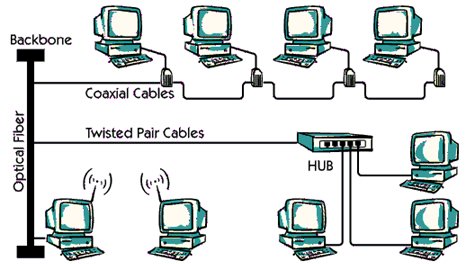
Cables:
Cables usually come in two flavors: ticked pair cables or coaxial cables.
Twisted pair cables
In a turning wire, there are two insulated strands of copper wire that are breaded. Often many twisted pairs are grouped together in a twisted pair cable. Twisted Jodi Cables is used for both data communication and telephony.
Coaxial cables
Coaxial cables have central operation copper cores that are surrounded by insulating material. Insulation is surrounded by a second operation layer, which may include Either a breaded wire net or a solid sleeve. In the picture, the coaxial cable will usually be Viewed on top should be used only for the network.
Optical fiber:
The optical fiber can be used to carry data signals in the form of modulated light beams with high bandwidth. Optical fiber has a very thin cylinder of glass, which is called The core is surrounded by a concentrated layer of glass. In the picture, the optical fiber will be Usually, the spinal cord should be used for the network.
Wired:
Different types of radio lanes are available on the market. This is an expensive type LAN TECHNICAL In the picture, the wireless connection is used between the two hosts Antenna Wireless LAN connections are often used in old historical buildings where you are Cable installation is not allowed.
Access Method
One feature is common for all local area networks that multiple hosts have to share Access to a physical transmission medium. Several methods can be employed to Control the sharing of access to the transmission medium.
Various access control methods can be marked in the network The transmission control function is performed. One access method can use the following forms Transmission control:
1. Random Control
Any host with random control can transmit and no permission is required. Can be a host Check the media to see if it is free or not before launching the transmission.
2. Distributed Control
With a distributed control, only one host has the right to communicate at a time and that's right.
Host passed to host. This is usually done by crossing a small piece called data token the host is the token, which is the right to send.
CSMA / CD
CSMA / CD stands for "Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision". CSMA / CD There is a random control access method.
CSMA / CD access method is used as an access control method in Ethernet and it is Defined from IEEE in a standard. CSMA / CD algorithm is quite simple and efficient About 65% for a normal Ethernet.
This means that the effective bandwidth for 10 Mbps Ethernet is approximately 6.5 Mbps. Due to the collision mainly, the rest have been lost.
Before a host is transmitted it should "listen" on the medium that there is no other host or not Transmitting If the medium is "cool" then the host can send its data. The term "career sense" Indicates that a host listens before transmitting.
"Multiple Access" means that many host networks and all hosts can be connected There is only one right to communicate.
With CSMA / CD, sometimes it happens that two hosts send their packets on it Time. It will collide on the network. There is information about the collision Discovered by all other hosts on the network. This is called "collision detection". If a host Detects the confrontation that it will wait for a random period before transmitting it again.
This picture shows what happened with the development of the two most used lanes Today technologies, Ethernet and token rings. 10 megabit Ethernet is present in two versions.
Digital version specified by two. Intel and Xerox, the most commonly used version, and IEEE standard 802.3 which is not commonly used. These are not two versions Compatible, because the frame format is different.
Fast Ethernet, which is specified in IEEE 802.3u, offers 100 Mbps. Fast Ethernet is one. The modern version of Ethernet and is often used in LAN spine networks (i.e. 1999) but is still not commonly used for customers.
Gigabit Ethernet on fiber, specified in IEEE 802.3z, provides 1000 Mbps. Gigabit Ethernet. Today is not so common (it is 1999). Gigabit Ethernet is used only in the LAN spine
Network because it is expensive and today there is no need for such high bandwidth Customers
Gigabit Ethernet on twist pair cable, specified in IEEE 802.3ab, offers 1000 Mbps. This standard is not fully specified today, which is in spring 1999.
Gigabit Ethernet is the future of LAN development because Ethernet is simple, reliable and Will be cheaper.
The token ring specified in IEEE 802.5 provides 4 and 16 Mbps. Use of token ring High-speed token ring, despite the new standard, to be offered, technology is decreasing 100 Mbps, has been specified.
Token passing
Another access method is used in the token ring, which is called token passing.
With a token passing, a small message, called a token, is constantly spread around the ring. If the token is marked for free, the host who receives the "free" token can transmit data Mark the token as busy. Receive all host data and busy token with the ring, Unless the original message sent does not free host the token again.
The token is now with Host B, and it has been marked for free. Let's say host B wants Host D. B sets the token to send data to the host and adds its data.
Host C now received token and data, but since there is no receiver Token and data pass in the ring.
Host D gets the data and sets the token to copy. Token and data are Passed in the ring.
Host A passes on tokens and data only.
Host B observes that the data has been received by DB in the proper manner so has been removed
Sets data and then tokens free.
Ethernet digital
Can use both Ethernet, Star and Bus topology defined in the IEEE 802.3 standard
Bandwidth between 10 and 100 Mbps Ethernet is the most common technology used today
In the local area network.
Digital uses Ethernet for communication between its products. This picture represents one
Initial implementation by digital You can see that Vax computers can be accessed by VT220
Terminal through a terminal server.
Ethernet sun
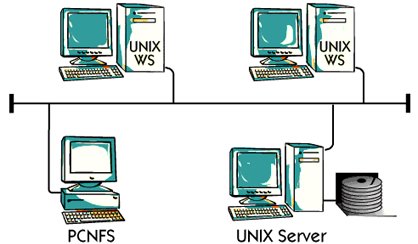
Sun Microsystems was one of the earliest manufacturers of Unix workstation. The sun was one
The initial sight is that "network is the computer" Sun is using Ethernet and TCP / IP as one
Strategic platform Since every Unix workstation and Unix server comes with ethernet
Card and TCP / IP software, it is ready for direct connections from the network.
For the PC market, Sun has developed PCNFS software so that a PC can communicate
With the Sun Tool
Ethernet in a mixed environment
Ethernet can be used to connect devices from different vendors. Can do different protocols Ethernet can also be used at the same time. For example, Novell's IPX / SPX can be used Together with TCP / IP Almost all modern computers, printers, and network components can Connect to Ethernet.
In this picture, you have three environments, Novell, Sun, and Digital, in Co-existence On an Ethernet at the same time Although these three cannot communicate with the environment In this configuration one second, they can still use the same Ethernet.
Token Ring
The token ring was introduced by IBM in 1987 and became its main architecture. The standard for the token ring from IEEE came in 1989.
Token Ring is the physical star and logical ring topology. This means that you connect Physically, computers in the star configuration in the hub, but the computers are still close Use the rights with the help of a token in a ring.
The bandwidth used in the token ring is 4 or 16 Mbps.
Token Ring IBM
In this picture, we see the IBM implementation of the token ring. An IBM Mainframe 30 9 0 Token rings cannot communicate directly with. To do this, it needs an NCP which is one A dedicated computer that only handles communication between mainframes and Token ring network
Users sitting on terminals can access data from mainframes via terminal Server. There are several thousand terminals connected to the mainframe.
Another possibility is to use a minicomputer such as AS / 400. These can be mini-computers Can be reached in the picture, or by terminals connected directly to the terminal server.
Token Ring Novel
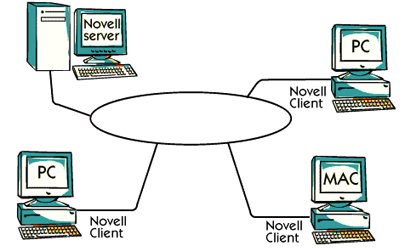
One common way for an organization to go from a mainframe to a modern computer is to Use the existing token ring network but to replace the previously used IBM devices computer.
Novell was the first person to see this market and he is using the token ring to connect Servers and customers together
In the picture, you can see a general configuration with different types of personal computers Working as Novell Client and Server
Token Ring in Mixed Environment
The token ring is mainly used to connect devices from IBM and Novell.
In this picture you have two environments, IBM and Novell are co-existing on a token ring. Although these two environments cannot communicate with each other in this Configuration, they can still use the same token ring.
FDDI
FDDI stands for Fiber Distributed Data Interface. The FDDI standard was developed by ANSI, American National Standards Institute. It is based on the use of double optical fiber cable And provides a token-passing ring configuration running at 100 Mbps.
FDDI is being developed to meet high-speed LANs, MANs, and requirements. Spinal cord network. Since FDDI has two fiber rings, primary and secondary ring, Good unnecessary and high availability.
Before a host is transmitted it should "listen" on the medium that there is no other host or not Transmitting If the medium is "cool" then the host can send its data. The term "career sense" Indicates that a host listens before transmitting.
"Multiple Access" means that many host networks and all hosts can be connected There is only one right to communicate.
With CSMA / CD, sometimes it happens that two hosts send their packets on it Time. It will collide on the network. There is information about the collision Discovered by all other hosts on the network. This is called "collision detection". If a host Detects the confrontation that it will wait for a random period before transmitting it again.
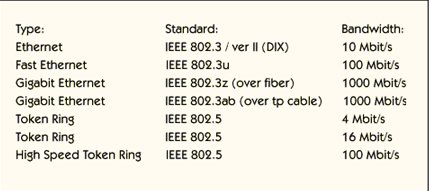
The development of the most popular LAN technologies
This picture shows what happened with the development of the two most used lanes Today technologies, Ethernet and token rings. 10 megabit Ethernet is present in two versions.
Digital version specified by two. Intel and Xerox, the most commonly used version, and IEEE standard 802.3 which is not commonly used. These are not two versions Compatible, because the frame format is different.
Fast Ethernet, which is specified in IEEE 802.3u, offers 100 Mbps. Fast Ethernet is one. The modern version of Ethernet and is often used in LAN spine networks (i.e. 1999) but is still not commonly used for customers.
Gigabit Ethernet on fiber, specified in IEEE 802.3z, provides 1000 Mbps. Gigabit Ethernet. Today is not so common (it is 1999). Gigabit Ethernet is used only in the LAN spine
Network because it is expensive and today there is no need for such high bandwidth Customers
Gigabit Ethernet on twist pair cable, specified in IEEE 802.3ab, offers 1000 Mbps. This standard is not fully specified today, which is in spring 1999.
Gigabit Ethernet is the future of LAN development because Ethernet is simple, reliable and Will be cheaper.
The token ring specified in IEEE 802.5 provides 4 and 16 Mbps. Use of token ring High-speed token ring, despite the new standard, to be offered, technology is decreasing 100 Mbps, has been specified.
Token passing
Another access method is used in the token ring, which is called token passing.
With a token passing, a small message, called a token, is constantly spread around the ring. If the token is marked for free, the host who receives the "free" token can transmit data Mark the token as busy. Receive all host data and busy token with the ring, Unless the original message sent does not free host the token again.
The token is now with Host B, and it has been marked for free. Let's say host B wants Host D. B sets the token to send data to the host and adds its data.
Host C now received token and data, but since there is no receiver Token and data pass in the ring.
Host D gets the data and sets the token to copy. Token and data are Passed in the ring.
Host A passes on tokens and data only.
Host B observes that the data has been received by DB in the proper manner so has been removed
Sets data and then tokens free.
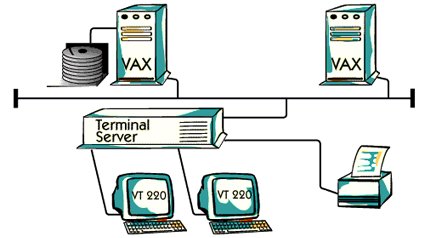
Ethernet digital
Can use both Ethernet, Star and Bus topology defined in the IEEE 802.3 standard
Bandwidth between 10 and 100 Mbps Ethernet is the most common technology used today
In the local area network.
Digital uses Ethernet for communication between its products. This picture represents one
Initial implementation by digital You can see that Vax computers can be accessed by VT220
Terminal through a terminal server.
Ethernet sun
Sun Microsystems was one of the earliest manufacturers of Unix workstation. The sun was one
The initial sight is that "network is the computer" Sun is using Ethernet and TCP / IP as one
Strategic platform Since every Unix workstation and Unix server comes with ethernet
Card and TCP / IP software, it is ready for direct connections from the network.
For the PC market, Sun has developed PCNFS software so that a PC can communicate
With the Sun Tool
Ethernet in a mixed environment
Ethernet can be used to connect devices from different vendors. Can do different protocols Ethernet can also be used at the same time. For example, Novell's IPX / SPX can be used Together with TCP / IP Almost all modern computers, printers, and network components can Connect to Ethernet.
In this picture, you have three environments, Novell, Sun, and Digital, in Co-existence On an Ethernet at the same time Although these three cannot communicate with the environment In this configuration one second, they can still use the same Ethernet.
Token Ring
The token ring was introduced by IBM in 1987 and became its main architecture. The standard for the token ring from IEEE came in 1989.
Token Ring is the physical star and logical ring topology. This means that you connect Physically, computers in the star configuration in the hub, but the computers are still close Use the rights with the help of a token in a ring.
The bandwidth used in the token ring is 4 or 16 Mbps.
Token Ring IBM
In this picture, we see the IBM implementation of the token ring. An IBM Mainframe 30 9 0 Token rings cannot communicate directly with. To do this, it needs an NCP which is one A dedicated computer that only handles communication between mainframes and Token ring network
Users sitting on terminals can access data from mainframes via terminal Server. There are several thousand terminals connected to the mainframe.
Another possibility is to use a minicomputer such as AS / 400. These can be mini-computers Can be reached in the picture, or by terminals connected directly to the terminal server.
Token Ring Novel
One common way for an organization to go from a mainframe to a modern computer is to Use the existing token ring network but to replace the previously used IBM devices computer.
Novell was the first person to see this market and he is using the token ring to connect Servers and customers together
In the picture, you can see a general configuration with different types of personal computers Working as Novell Client and Server
Token Ring in Mixed Environment
The token ring is mainly used to connect devices from IBM and Novell.
In this picture you have two environments, IBM and Novell are co-existing on a token ring. Although these two environments cannot communicate with each other in this Configuration, they can still use the same token ring.
FDDI
FDDI stands for Fiber Distributed Data Interface. The FDDI standard was developed by ANSI, American National Standards Institute. It is based on the use of double optical fiber cable And provides a token-passing ring configuration running at 100 Mbps.
FDDI is being developed to meet high-speed LANs, MANs, and requirements. Spinal cord network. Since FDDI has two fiber rings, primary and secondary ring, Good unnecessary and high availability.
Typically traffic flows only on the primary Ring, but if the primary ring is broken then the secondary ring is used.
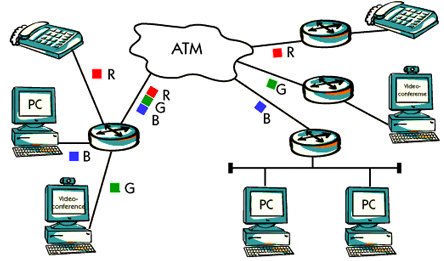
ATM
ATM, which stands for Asynchronous Transfer Mode, has developed a "real fact" ATM is a switching method forum and communication, which can be used both in LAN and VAN
ATM specifications are being written to ensure that ATM easily integrates many Existing Network Technologies
Today, in many cases, different networks are used to move voice, data, and video. Information, mostly because these traffic types have different features. for example, Data traffic is "explosion", whereas voice and video are more "continuous".
ATM
ATM, which stands for Asynchronous Transfer Mode, has developed a "real fact" ATM is a switching method forum and communication, which can be used both in LAN and VAN
ATM specifications are being written to ensure that ATM easily integrates many Existing Network Technologies
Today, in many cases, different networks are used to move voice, data, and video. Information, mostly because these traffic types have different features. for example, Data traffic is "explosion", whereas voice and video are more "continuous".
With ATM, separate networks will not be required. ATM is the only technology that From the beginning, the data was designed to adjust the transmission simultaneously, Voice and video
ATMs are available at various speeds, but usually, 25, 155, and 622 Mbps are used.
Components of LAN
A hub is a commonly used device to connect a host with a bus or ring. Topology Each host is connected to a hub through a port. When a hub receives a signal on a port It sends signals to all other ports. Many hubs are weak and weak Sign them again before remitting them.
A switch is a multiport device that handles routing between different hosts on their basis MAC Addresses A switch "learns" the mac address from those hosts that are connected Switch, and store them in an internal table. When two hosts communicate with each other, The switch creates a temporary connection path between them.
This means that only two hosts will listen to each other and not like the hub, where everyone listens. For example, if Host A and Host interact with each other, Host C and D can communicate at the same time without any problems from Host A and B.
ATMs are available at various speeds, but usually, 25, 155, and 622 Mbps are used.
Components of LAN
A hub is a commonly used device to connect a host with a bus or ring. Topology Each host is connected to a hub through a port. When a hub receives a signal on a port It sends signals to all other ports. Many hubs are weak and weak Sign them again before remitting them.
A switch is a multiport device that handles routing between different hosts on their basis MAC Addresses A switch "learns" the mac address from those hosts that are connected Switch, and store them in an internal table. When two hosts communicate with each other, The switch creates a temporary connection path between them.
This means that only two hosts will listen to each other and not like the hub, where everyone listens. For example, if Host A and Host interact with each other, Host C and D can communicate at the same time without any problems from Host A and B.
The possibility of a host for the broadcast, which means that the packet will be broadcast on all
Ports in the switch.
Switches improve the performance of a LAN in two ways. Firstly they increase the available
Bandwidth for each host, because avoids the collision.
Ports in the switch.
Switches improve the performance of a LAN in two ways. Firstly they increase the available
Bandwidth for each host, because avoids the collision.
The second is an improvement in Security. A user on a host connected through a hub, using sniffer software, can listen to other Conversations. This is not possible in the switched network.
Switching Methods
Fast Moving
Fast forward or cut-through switching packet is the fastest way to forward Switch. As soon as the switch is able to determine the switch moves the packet forward Destination MAC Address Although it usually reduces network latency, it proceeds quickly Switching does not verify the checksum and as a result, it is allowed to pass bad packets, which Can reduce the available bandwidth.
Switching Methods
Fast Moving
Fast forward or cut-through switching packet is the fastest way to forward Switch. As soon as the switch is able to determine the switch moves the packet forward Destination MAC Address Although it usually reduces network latency, it proceeds quickly Switching does not verify the checksum and as a result, it is allowed to pass bad packets, which Can reduce the available bandwidth.
Never switching fast forward
Which means that the two hosts can send each other together Moves towards confrontation.
Store and Forward
The switch and switch switching switch in the store waits till the full packet is not received first Send it to the destination.
Which means that the two hosts can send each other together Moves towards confrontation.
Store and Forward
The switch and switch switching switch in the store waits till the full packet is not received first Send it to the destination.
This allows the switch to verify and eliminate the packet's checksum Possibility to forward bad packets While the packet is stored in the buffer Switch, transmission direction is established, which means that there can be no collision.
A disadvantage with the store and forwarding switching is that there is a delay because of the switch Time to buffer and analyze packets is required.
Piece Free
The segment-free switch works like fast forward, but it buffers 64 bytes of each Packet to avoid a collision.
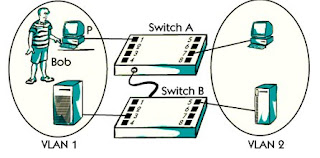
VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network)
A switch makes it possible to configure something called VLAN. A VLAN, which stands Virtual Local Area Network is a logical LAN that includes host groups. A physical The LAN can be divided into several VLANs.
Piece Free
The segment-free switch works like fast forward, but it buffers 64 bytes of each Packet to avoid a collision.
VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network)
A switch makes it possible to configure something called VLAN. A VLAN, which stands Virtual Local Area Network is a logical LAN that includes host groups. A physical The LAN can be divided into several VLANs.
A VLAN can be configured by one or several Switch, which can be geographically distributed but is a logical Presence Users of the same VLAN can communicate with each other at LAN speeds With router latency
There are various solutions for communication between VLANs, but the most common use the router. Sometimes the router integrates into the switch.
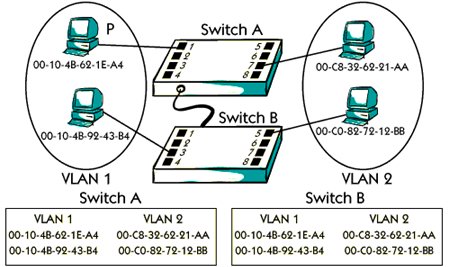
Port-based VLAN
There are many different solutions to make VLAN. The port-based solution means that A
The host is related to a special VLAN, depending on which is the physical port in the host switch
Connected to For example, in the photo, the host P is connected to the P4 port of A, Which means that host P related to VLAN.
Mac-based VLAN
Mac-based VLAN means that a host belongs to a particular VLAN, which is based on Mac The host is aware. Mac-based VLAN is independent of which physical switch port Is connected to the host.
There are various solutions for communication between VLANs, but the most common use the router. Sometimes the router integrates into the switch.
Port-based VLAN
There are many different solutions to make VLAN. The port-based solution means that A
The host is related to a special VLAN, depending on which is the physical port in the host switch
Connected to For example, in the photo, the host P is connected to the P4 port of A, Which means that host P related to VLAN.
Mac-based VLAN
Mac-based VLAN means that a host belongs to a particular VLAN, which is based on Mac The host is aware. Mac-based VLAN is independent of which physical switch port Is connected to the host.
For example, the MAC address in Host P in the photo 00-10-4- B-62-1E-A4, which means that host P is related to VLAN1, as can be seen in the left table.
As you can see, the same MAC address of host P is also in the table for switch B This means that if we connect host P to any port of Switch B, then host P will still be related to VLAN
Protocol-based VLAN
Protocol-based VLAN means that a host is related to a particular VLAN on the basis of which The protocol uses it for communication. For example, in the photo Host is P Netware The client usually uses the IPX protocol, which means that it is related to IPX VLAN.
User-based VLAN
There will be other VLAN solutions in the future. A promotion solution, many Waiting for people, user-based VLAN. When a user identifies a particular host on a particular host Used by the switch and then the host becomes part of a special for VLAN.
For example, user Bob logs in the picture with his own user ID and password on Host P.
Switch A decides that Bob belongs to VLAN.
See: What is Blockchain Technology?
See: How to Google?
Protocol-based VLAN
Protocol-based VLAN means that a host is related to a particular VLAN on the basis of which The protocol uses it for communication. For example, in the photo Host is P Netware The client usually uses the IPX protocol, which means that it is related to IPX VLAN.
User-based VLAN
There will be other VLAN solutions in the future. A promotion solution, many Waiting for people, user-based VLAN. When a user identifies a particular host on a particular host Used by the switch and then the host becomes part of a special for VLAN.
For example, user Bob logs in the picture with his own user ID and password on Host P.
Switch A decides that Bob belongs to VLAN.
See: What is Blockchain Technology?
See: How to Google?
Labels:
Networking
 Hi'i'm Rahim Ansari ,from India, I Love to Blogging, Desing Website, Web Developing and Desiging I Like to Learn and share Technical Hacking/Security tips with you,I Love my Friends.
Hi'i'm Rahim Ansari ,from India, I Love to Blogging, Desing Website, Web Developing and Desiging I Like to Learn and share Technical Hacking/Security tips with you,I Love my Friends.