What is LAN? (Local Area Network)
History of LAN (Local Area Network)
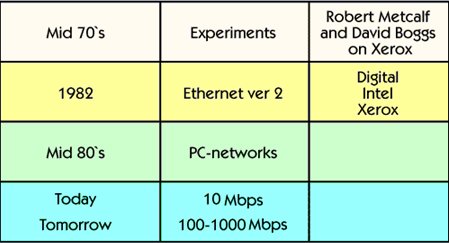
In the mid-'70s, Robert Metcalfe and Xerox used David Boggs with communication Between computers, This became the first implementation of Ethernet.
In 1982, the second edition of Ethernet was implemented by Digital, Intel, and Xerox. This is The version of Ethernet that is still in use.
In the mid-'80s, the first PC-networks were visible. Such as network components Bridges and routers were now available on the market.
The local bandwidth of the local area network is 10 Mbps today.
Topology
The network's topology deals with the physical configuration of devices and cables
Which connects them.
There are three Topologies are used for Local Area Networks(LAN):
1. Bus network: All connected hosts are just sharing the same cable on the network. All hosts should be used
The same communication speed and "listen" all the traffic on each host cable.
2. Ring Network: All hosts in the ring topology are connected in a ring. Each host receives all the data in the ring
If there is any other destination information for the data, then the host will re-send the data.
The data will continue to travel as long as the destination does not reach the destination host.
3. Star Network: A star configuration consists of a central controller that can be a hub or switch. Each host is directly connected to a port on the central controller.
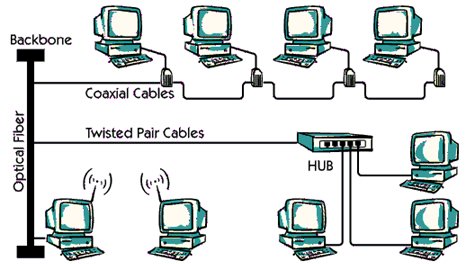
Transmission Media
The IEEE standard for LAN describes various types of transmission media. It can be cable, fiber or wireless.
Cables:
Cables usually come in two flavors: ticked pair cables or coaxial cables.
Twisted pair cables
In a turning wire, there are two insulated strands of copper wire that are breaded. Often many twisted pairs are grouped together in a twisted pair cable. Twisted Jodi Cables is used for both data communication and telephony.
Coaxial cables
Coaxial cables have central operation copper cores that are surrounded by insulating material. Insulation is surrounded by a second operation layer, which may include Either a breaded wire net or a solid sleeve. In the picture, the coaxial cable will usually be Viewed on top should be used only for the network.
Optical fiber:
The optical fiber can be used to carry data signals in the form of modulated light beams with high bandwidth. Optical fiber has a very thin cylinder of glass, which is called The core is surrounded by a concentrated layer of glass. In the picture, the optical fiber will be Usually, the spinal cord should be used for the network.
Wired:
Different types of radio lanes are available on the market. This is an expensive type LAN TECHNICAL In the picture, the wireless connection is used between the two hosts Antenna Wireless LAN connections are often used in old historical buildings where you are Cable installation is not allowed.
Access Method
One feature is common for all local area networks that multiple hosts have to share Access to a physical transmission medium. Several methods can be employed to Control the sharing of access to the transmission medium.
Various access control methods can be marked in the network The transmission control function is performed. One access method can use the following forms Transmission control:
1. Random Control
Any host with random control can transmit and no permission is required. Can be a host Check the media to see if it is free or not before launching the transmission.
2. Distributed Control
With a distributed control, only one host has the right to communicate at a time and that's right.
Host passed to host. This is usually done by crossing a small piece called data token the host is the token, which is the right to send.
CSMA / CD
CSMA / CD stands for "Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision". CSMA / CD There is a random control access method.
CSMA / CD access method is used as an access control method in Ethernet and it is Defined from IEEE in a standard. CSMA / CD algorithm is quite simple and efficient About 65% for a normal Ethernet.
This means that the effective bandwidth for 10 Mbps Ethernet is approximately 6.5 Mbps. Due to the collision mainly, the rest have been lost.
Before a host is transmitted it should "listen" on the medium that there is no other host or not Transmitting If the medium is "cool" then the host can send its data. The term "career sense" Indicates that a host listens before transmitting.
"Multiple Access" means that many host networks and all hosts can be connected There is only one right to communicate.
With CSMA / CD, sometimes it happens that two hosts send their packets on it Time. It will collide on the network. There is information about the collision Discovered by all other hosts on the network. This is called "collision detection". If a host Detects the confrontation that it will wait for a random period before transmitting it again.
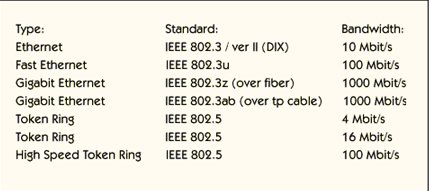
This picture shows what happened with the development of the two most used lanes Today technologies, Ethernet and token rings. 10 megabit Ethernet is present in two versions.
Digital version specified by two. Intel and Xerox, the most commonly used version, and IEEE standard 802.3 which is not commonly used. These are not two versions Compatible, because the frame format is different.
Fast Ethernet, which is specified in IEEE 802.3u, offers 100 Mbps. Fast Ethernet is one. The modern version of Ethernet and is often used in LAN spine networks (i.e. 1999) but is still not commonly used for customers.
Gigabit Ethernet on fiber, specified in IEEE 802.3z, provides 1000 Mbps. Gigabit Ethernet. Today is not so common (it is 1999). Gigabit Ethernet is used only in the LAN spine
Network because it is expensive and today there is no need for such high bandwidth Customers
Gigabit Ethernet on twist pair cable, specified in IEEE 802.3ab, offers 1000 Mbps. This standard is not fully specified today, which is in spring 1999.
Gigabit Ethernet is the future of LAN development because Ethernet is simple, reliable and Will be cheaper.
The token ring specified in IEEE 802.5 provides 4 and 16 Mbps. Use of token ring High-speed token ring, despite the new standard, to be offered, technology is decreasing 100 Mbps, has been specified.
Token passing
Another access method is used in the token ring, which is called token passing.
With a token passing, a small message, called a token, is constantly spread around the ring. If the token is marked for free, the host who receives the "free" token can transmit data Mark the token as busy. Receive all host data and busy token with the ring, Unless the original message sent does not free host the token again.
The token is now with Host B, and it has been marked for free. Let's say host B wants Host D. B sets the token to send data to the host and adds its data.
Host C now received token and data, but since there is no receiver Token and data pass in the ring.
Host D gets the data and sets the token to copy. Token and data are Passed in the ring.
Host A passes on tokens and data only.
Host B observes that the data has been received by DB in the proper manner so has been removed
Sets data and then tokens free.
Ethernet digital
Can use both Ethernet, Star and Bus topology defined in the IEEE 802.3 standard
Bandwidth between 10 and 100 Mbps Ethernet is the most common technology used today
In the local area network.
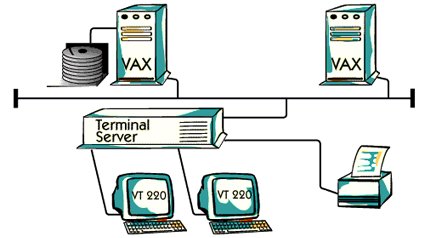
Digital uses Ethernet for communication between its products. This picture represents one
Initial implementation by digital You can see that Vax computers can be accessed by VT220
Terminal through a terminal server.
Ethernet sun
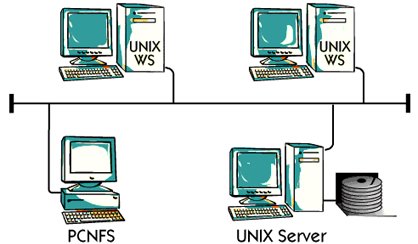
Sun Microsystems was one of the earliest manufacturers of Unix workstation. The sun was one
The initial sight is that "network is the computer" Sun is using Ethernet and TCP / IP as one
Strategic platform Since every Unix workstation and Unix server comes with ethernet
Card and TCP / IP software, it is ready for direct connections from the network.
For the PC market, Sun has developed PCNFS software so that a PC can communicate
With the Sun Tool
Ethernet in a mixed environment
Ethernet can be used to connect devices from different vendors. Can do different protocols Ethernet can also be used at the same time. For example, Novell's IPX / SPX can be used Together with TCP / IP Almost all modern computers, printers, and network components can Connect to Ethernet.
In this picture, you have three environments, Novell, Sun, and Digital, in Co-existence On an Ethernet at the same time Although these three cannot communicate with the environment In this configuration one second, they can still use the same Ethernet.
Token Ring
The token ring was introduced by IBM in 1987 and became its main architecture. The standard for the token ring from IEEE came in 1989.
Token Ring is the physical star and logical ring topology. This means that you connect Physically, computers in the star configuration in the hub, but the computers are still close Use the rights with the help of a token in a ring.
The bandwidth used in the token ring is 4 or 16 Mbps.
Token Ring IBM
In this picture, we see the IBM implementation of the token ring. An IBM Mainframe 30 9 0 Token rings cannot communicate directly with. To do this, it needs an NCP which is one A dedicated computer that only handles communication between mainframes and Token ring network
Users sitting on terminals can access data from mainframes via terminal Server. There are several thousand terminals connected to the mainframe.
Another possibility is to use a minicomputer such as AS / 400. These can be mini-computers Can be reached in the picture, or by terminals connected directly to the terminal server.
Token Ring Novel
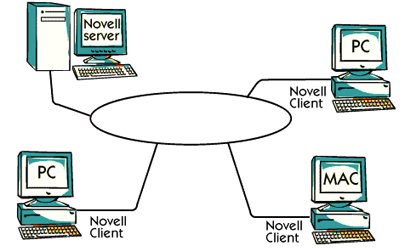
One common way for an organization to go from a mainframe to a modern computer is to Use the existing token ring network but to replace the previously used IBM devices computer.
Novell was the first person to see this market and he is using the token ring to connect Servers and customers together
In the picture, you can see a general configuration with different types of personal computers Working as Novell Client and Server
Token Ring in Mixed Environment
The token ring is mainly used to connect devices from IBM and Novell.
In this picture you have two environments, IBM and Novell are co-existing on a token ring. Although these two environments cannot communicate with each other in this Configuration, they can still use the same token ring.
FDDI
FDDI stands for Fiber Distributed Data Interface. The FDDI standard was developed by ANSI, American National Standards Institute. It is based on the use of double optical fiber cable And provides a token-passing ring configuration running at 100 Mbps.
FDDI is being developed to meet high-speed LANs, MANs, and requirements. Spinal cord network. Since FDDI has two fiber rings, primary and secondary ring, Good unnecessary and high availability.
Before a host is transmitted it should "listen" on the medium that there is no other host or not Transmitting If the medium is "cool" then the host can send its data. The term "career sense" Indicates that a host listens before transmitting.
"Multiple Access" means that many host networks and all hosts can be connected There is only one right to communicate.
With CSMA / CD, sometimes it happens that two hosts send their packets on it Time. It will collide on the network. There is information about the collision Discovered by all other hosts on the network. This is called "collision detection". If a host Detects the confrontation that it will wait for a random period before transmitting it again.
The development of the most popular LAN technologies
This picture shows what happened with the development of the two most used lanes Today technologies, Ethernet and token rings. 10 megabit Ethernet is present in two versions.
Digital version specified by two. Intel and Xerox, the most commonly used version, and IEEE standard 802.3 which is not commonly used. These are not two versions Compatible, because the frame format is different.
Fast Ethernet, which is specified in IEEE 802.3u, offers 100 Mbps. Fast Ethernet is one. The modern version of Ethernet and is often used in LAN spine networks (i.e. 1999) but is still not commonly used for customers.
Gigabit Ethernet on fiber, specified in IEEE 802.3z, provides 1000 Mbps. Gigabit Ethernet. Today is not so common (it is 1999). Gigabit Ethernet is used only in the LAN spine
Network because it is expensive and today there is no need for such high bandwidth Customers
Gigabit Ethernet on twist pair cable, specified in IEEE 802.3ab, offers 1000 Mbps. This standard is not fully specified today, which is in spring 1999.
Gigabit Ethernet is the future of LAN development because Ethernet is simple, reliable and Will be cheaper.
The token ring specified in IEEE 802.5 provides 4 and 16 Mbps. Use of token ring High-speed token ring, despite the new standard, to be offered, technology is decreasing 100 Mbps, has been specified.
Token passing
Another access method is used in the token ring, which is called token passing.
With a token passing, a small message, called a token, is constantly spread around the ring. If the token is marked for free, the host who receives the "free" token can transmit data Mark the token as busy. Receive all host data and busy token with the ring, Unless the original message sent does not free host the token again.
The token is now with Host B, and it has been marked for free. Let's say host B wants Host D. B sets the token to send data to the host and adds its data.
Host C now received token and data, but since there is no receiver Token and data pass in the ring.
Host D gets the data and sets the token to copy. Token and data are Passed in the ring.
Host A passes on tokens and data only.
Host B observes that the data has been received by DB in the proper manner so has been removed
Sets data and then tokens free.
Ethernet digital
Can use both Ethernet, Star and Bus topology defined in the IEEE 802.3 standard
Bandwidth between 10 and 100 Mbps Ethernet is the most common technology used today
In the local area network.
Digital uses Ethernet for communication between its products. This picture represents one
Initial implementation by digital You can see that Vax computers can be accessed by VT220
Terminal through a terminal server.
Ethernet sun
Sun Microsystems was one of the earliest manufacturers of Unix workstation. The sun was one
The initial sight is that "network is the computer" Sun is using Ethernet and TCP / IP as one
Strategic platform Since every Unix workstation and Unix server comes with ethernet
Card and TCP / IP software, it is ready for direct connections from the network.
For the PC market, Sun has developed PCNFS software so that a PC can communicate
With the Sun Tool
Ethernet in a mixed environment
Ethernet can be used to connect devices from different vendors. Can do different protocols Ethernet can also be used at the same time. For example, Novell's IPX / SPX can be used Together with TCP / IP Almost all modern computers, printers, and network components can Connect to Ethernet.
In this picture, you have three environments, Novell, Sun, and Digital, in Co-existence On an Ethernet at the same time Although these three cannot communicate with the environment In this configuration one second, they can still use the same Ethernet.
Token Ring
The token ring was introduced by IBM in 1987 and became its main architecture. The standard for the token ring from IEEE came in 1989.
Token Ring is the physical star and logical ring topology. This means that you connect Physically, computers in the star configuration in the hub, but the computers are still close Use the rights with the help of a token in a ring.
The bandwidth used in the token ring is 4 or 16 Mbps.
Token Ring IBM
In this picture, we see the IBM implementation of the token ring. An IBM Mainframe 30 9 0 Token rings cannot communicate directly with. To do this, it needs an NCP which is one A dedicated computer that only handles communication between mainframes and Token ring network
Users sitting on terminals can access data from mainframes via terminal Server. There are several thousand terminals connected to the mainframe.
Another possibility is to use a minicomputer such as AS / 400. These can be mini-computers Can be reached in the picture, or by terminals connected directly to the terminal server.
Token Ring Novel
One common way for an organization to go from a mainframe to a modern computer is to Use the existing token ring network but to replace the previously used IBM devices computer.
Novell was the first person to see this market and he is using the token ring to connect Servers and customers together
In the picture, you can see a general configuration with different types of personal computers Working as Novell Client and Server
Token Ring in Mixed Environment
The token ring is mainly used to connect devices from IBM and Novell.
In this picture you have two environments, IBM and Novell are co-existing on a token ring. Although these two environments cannot communicate with each other in this Configuration, they can still use the same token ring.
FDDI
FDDI stands for Fiber Distributed Data Interface. The FDDI standard was developed by ANSI, American National Standards Institute. It is based on the use of double optical fiber cable And provides a token-passing ring configuration running at 100 Mbps.
FDDI is being developed to meet high-speed LANs, MANs, and requirements. Spinal cord network. Since FDDI has two fiber rings, primary and secondary ring, Good unnecessary and high availability.
Typically traffic flows only on the primary Ring, but if the primary ring is broken then the secondary ring is used.
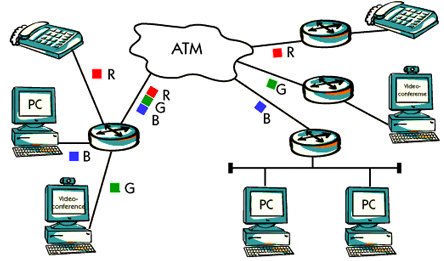
ATM
ATM, which stands for Asynchronous Transfer Mode, has developed a "real fact" ATM is a switching method forum and communication, which can be used both in LAN and VAN
ATM specifications are being written to ensure that ATM easily integrates many Existing Network Technologies
Today, in many cases, different networks are used to move voice, data, and video. Information, mostly because these traffic types have different features. for example, Data traffic is "explosion", whereas voice and video are more "continuous".
ATM
ATM, which stands for Asynchronous Transfer Mode, has developed a "real fact" ATM is a switching method forum and communication, which can be used both in LAN and VAN
ATM specifications are being written to ensure that ATM easily integrates many Existing Network Technologies
Today, in many cases, different networks are used to move voice, data, and video. Information, mostly because these traffic types have different features. for example, Data traffic is "explosion", whereas voice and video are more "continuous".
With ATM, separate networks will not be required. ATM is the only technology that From the beginning, the data was designed to adjust the transmission simultaneously, Voice and video
ATMs are available at various speeds, but usually, 25, 155, and 622 Mbps are used.
Components of LAN
A hub is a commonly used device to connect a host with a bus or ring. Topology Each host is connected to a hub through a port. When a hub receives a signal on a port It sends signals to all other ports. Many hubs are weak and weak Sign them again before remitting them.
A switch is a multiport device that handles routing between different hosts on their basis MAC Addresses A switch "learns" the mac address from those hosts that are connected Switch, and store them in an internal table. When two hosts communicate with each other, The switch creates a temporary connection path between them.
This means that only two hosts will listen to each other and not like the hub, where everyone listens. For example, if Host A and Host interact with each other, Host C and D can communicate at the same time without any problems from Host A and B.
ATMs are available at various speeds, but usually, 25, 155, and 622 Mbps are used.
Components of LAN
A hub is a commonly used device to connect a host with a bus or ring. Topology Each host is connected to a hub through a port. When a hub receives a signal on a port It sends signals to all other ports. Many hubs are weak and weak Sign them again before remitting them.
A switch is a multiport device that handles routing between different hosts on their basis MAC Addresses A switch "learns" the mac address from those hosts that are connected Switch, and store them in an internal table. When two hosts communicate with each other, The switch creates a temporary connection path between them.
This means that only two hosts will listen to each other and not like the hub, where everyone listens. For example, if Host A and Host interact with each other, Host C and D can communicate at the same time without any problems from Host A and B.
The possibility of a host for the broadcast, which means that the packet will be broadcast on all
Ports in the switch.
Switches improve the performance of a LAN in two ways. Firstly they increase the available
Bandwidth for each host, because avoids the collision.
Ports in the switch.
Switches improve the performance of a LAN in two ways. Firstly they increase the available
Bandwidth for each host, because avoids the collision.
The second is an improvement in Security. A user on a host connected through a hub, using sniffer software, can listen to other Conversations. This is not possible in the switched network.
Switching Methods
Fast Moving
Fast forward or cut-through switching packet is the fastest way to forward Switch. As soon as the switch is able to determine the switch moves the packet forward Destination MAC Address Although it usually reduces network latency, it proceeds quickly Switching does not verify the checksum and as a result, it is allowed to pass bad packets, which Can reduce the available bandwidth.
Switching Methods
Fast Moving
Fast forward or cut-through switching packet is the fastest way to forward Switch. As soon as the switch is able to determine the switch moves the packet forward Destination MAC Address Although it usually reduces network latency, it proceeds quickly Switching does not verify the checksum and as a result, it is allowed to pass bad packets, which Can reduce the available bandwidth.
Never switching fast forward
Which means that the two hosts can send each other together Moves towards confrontation.
Store and Forward
The switch and switch switching switch in the store waits till the full packet is not received first Send it to the destination.
Which means that the two hosts can send each other together Moves towards confrontation.
Store and Forward
The switch and switch switching switch in the store waits till the full packet is not received first Send it to the destination.
This allows the switch to verify and eliminate the packet's checksum Possibility to forward bad packets While the packet is stored in the buffer Switch, transmission direction is established, which means that there can be no collision.
A disadvantage with the store and forwarding switching is that there is a delay because of the switch Time to buffer and analyze packets is required.
Piece Free
The segment-free switch works like fast forward, but it buffers 64 bytes of each Packet to avoid a collision.
VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network)
A switch makes it possible to configure something called VLAN. A VLAN, which stands Virtual Local Area Network is a logical LAN that includes host groups. A physical The LAN can be divided into several VLANs.
Piece Free
The segment-free switch works like fast forward, but it buffers 64 bytes of each Packet to avoid a collision.
VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network)
A switch makes it possible to configure something called VLAN. A VLAN, which stands Virtual Local Area Network is a logical LAN that includes host groups. A physical The LAN can be divided into several VLANs.
A VLAN can be configured by one or several Switch, which can be geographically distributed but is a logical Presence Users of the same VLAN can communicate with each other at LAN speeds With router latency
There are various solutions for communication between VLANs, but the most common use the router. Sometimes the router integrates into the switch.
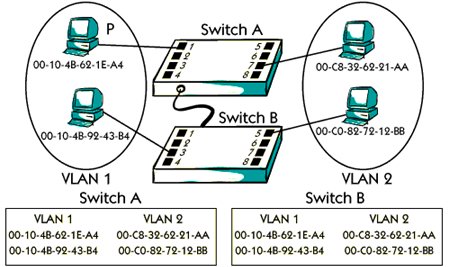
Port-based VLAN
There are many different solutions to make VLAN. The port-based solution means that A
The host is related to a special VLAN, depending on which is the physical port in the host switch
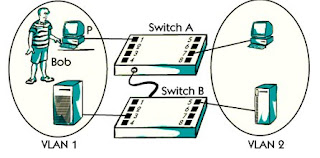
Connected to For example, in the photo, the host P is connected to the P4 port of A, Which means that host P related to VLAN.
Mac-based VLAN
Mac-based VLAN means that a host belongs to a particular VLAN, which is based on Mac The host is aware. Mac-based VLAN is independent of which physical switch port Is connected to the host.
There are various solutions for communication between VLANs, but the most common use the router. Sometimes the router integrates into the switch.
Port-based VLAN
There are many different solutions to make VLAN. The port-based solution means that A
The host is related to a special VLAN, depending on which is the physical port in the host switch
Connected to For example, in the photo, the host P is connected to the P4 port of A, Which means that host P related to VLAN.
Mac-based VLAN
Mac-based VLAN means that a host belongs to a particular VLAN, which is based on Mac The host is aware. Mac-based VLAN is independent of which physical switch port Is connected to the host.
For example, the MAC address in Host P in the photo 00-10-4- B-62-1E-A4, which means that host P is related to VLAN1, as can be seen in the left table.
As you can see, the same MAC address of host P is also in the table for switch B This means that if we connect host P to any port of Switch B, then host P will still be related to VLAN
Protocol-based VLAN
Protocol-based VLAN means that a host is related to a particular VLAN on the basis of which The protocol uses it for communication. For example, in the photo Host is P Netware The client usually uses the IPX protocol, which means that it is related to IPX VLAN.
User-based VLAN
There will be other VLAN solutions in the future. A promotion solution, many Waiting for people, user-based VLAN. When a user identifies a particular host on a particular host Used by the switch and then the host becomes part of a special for VLAN.
For example, user Bob logs in the picture with his own user ID and password on Host P.
Switch A decides that Bob belongs to VLAN.
See: What is Blockchain Technology?
See: How to Google?
Protocol-based VLAN
Protocol-based VLAN means that a host is related to a particular VLAN on the basis of which The protocol uses it for communication. For example, in the photo Host is P Netware The client usually uses the IPX protocol, which means that it is related to IPX VLAN.
User-based VLAN
There will be other VLAN solutions in the future. A promotion solution, many Waiting for people, user-based VLAN. When a user identifies a particular host on a particular host Used by the switch and then the host becomes part of a special for VLAN.
For example, user Bob logs in the picture with his own user ID and password on Host P.
Switch A decides that Bob belongs to VLAN.
See: What is Blockchain Technology?
See: How to Google?


.png)




























No comments:
Post a Comment