What is TCP/IP and How TCP/IP Works?
What is TCP /IP? (Transmission Control Protocol)
Overview of TCP / IP
An open network architecture that supports routing and controlled transmission on global and local networks
- Supported by almost all computer vendors
- Continuous development of TCP / IP standard
- Important Technology for the Internet
TCP / IP is also used on both global networks, such as the Internet and local area networks.
TCP / IP is an open communication architecture which is widely spread. Implementation of TCP / IP for most common types of computers.
TCP / IP was developed to connect hosts on ARPANET, which was the first implementation of the Internet. ARPANET has retired, but TCP / IP continues and is constantly being developed with new standards.
TCP / IP is currently used on the Internet where it is used as a major technology. Popular protocols in the TCP / IP family are SMTP, which is a simple Mail Transfer Protocol, FTP, for File Transfer Protocol and Telnet Protocol, which is used for remote access.
History of TCP / IP
The TCP / IP United States detects its origins for a research project funded by DARPA, which is for the Defense Advanced Research Project Agency. As a result of this project, in 1969 an experimental network called ARPANET was formed. In 1975, ARPANET was put into operation, the experiment proved to be successful after it was successful. The protocol used was called NCP, which stood for the Network Control Protocol.
In 1979, the development of a new protocol suite called TCP / IP started. Many thoughts came from the NCP in the TCP / IP protocol.
In 1983, the new protocol called TCP / IP was adopted as a suite standard, and all the hosts on ARPANET needed to use it.
In 1984, ARPANET was divided into separate networks and the word was used instead of ARPANET.
In 1987, the internet was spread all over the world.
Today Internet Protocol is hindered for future development. A new version of Internet Protocol is called IPv6, which stands for IP version 6, is now standardized. This will provide great address space and support for quality of service multimedia applications.
Internet
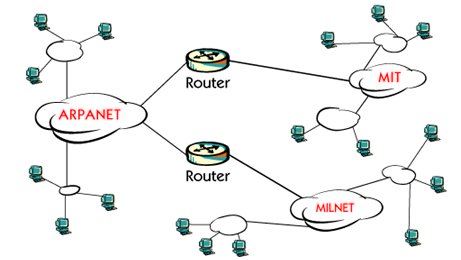
DARPA started its work around 1969. DARPA was well-known for its ideas about secure packet-switched networks, and the result was famous ARPANET in 1975.
Many researchers involved in ARPANET. 1979 DARPA created a committee called Internet Control and Configuration Board, ICCB, which later became the Internet Architectural Board, IAB. In 1983, ARPANET was divided into two separate networks, one for research and one for military use.
The research network was still called ARPANET and the military part was called MILINET. At this time TCP / IP architecture was established and used. Also, the router technology was developed and used to isolate it individually
Network
Later in the United States, several high schools and universities were connected to this network. One example was the MIT, Massachusetts Institute of Technology. It was the beginning of the Internet.
Internet Standard
To handle all the standards required for TCP / IP architecture and Internet communication, the standardization organization was required.
As an umbrella organization for standardization, ISOC is for the Internet Society. The IAB is below the Internet Architectural Board, ISOC. IAB consists of 16 members of various companies or service providers. IAB is responsible for making standard proposals in official standards. Standard proposals are called RFCs, which means
Request for Comments. Today there are around 2200 different RFCs. Some of them are only for historical use, some are for experimental use and some are for official use.
There are three famous groups under IAB.
First, IETF is the Internet Engineering Task Force, which includes various executive groups who test all protocols before getting the final standard status by IAB.
The second is IANA, the Internet Assignment Number Authority, which is responsible for an RFC document called Assign Number. This RFC specifies different numbers for different protocols used in data communication.
The third is an IRTF, the Internet Research Task Force, which includes various research groups looking into the future; What is going to happen with the Internet and TCP / IP architecture?
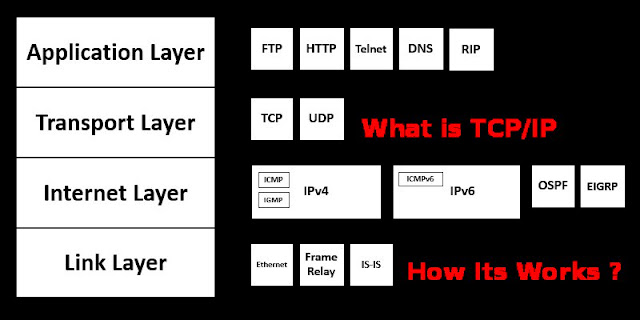
TCP / IP Family Architecture and Protocol
TCP / IP architecture includes only four layers.
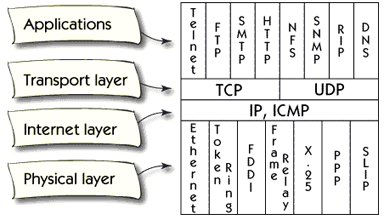
There is a correspondence between the OSI model and layers in TCP / IP.
Layer One and Two which are physical and data link layers in the OSI model correspond to the physical layer of TCP / IP.
The network layer in the OSI model which is the layer three corresponds to the Internet layer of TCP/IP
The layer four is called the transport layer in both models.
Layer five, six and seven in the OSI model are included in the application layer of all TCP / IP architecture.
The physical layer describes the interface for different types of networks, such as Ethernet, Token Ring, and X25.
Internet layer describes Internet Protocol or IP. Internet Control Message Protocol, ICMP, is a support protocol for IP. It is used to send feedback information on the IP protocol, for example, if something goes wrong.
Transport layer describes two protocols; Transmission Control Protocol, TCP and User Datagram Protocol, UDP. Both of these protocols take the data to the correct session, but TCP does it in a reliable manner, and the UDP is unreliable.
The application layer contains hundreds of application protocols. Telnet, FTP, SMTP, and HTTP are the most common.
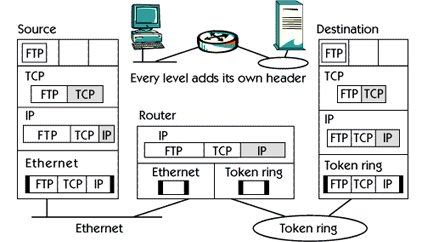
Traffic Flow
In the picture, you see a file transfer session between the source and destination host. The source host adds some extra header information to each layer. The destination host reduces this header information if everything is received properly.
In the FTP Data Transport Layer, the Transport Protocol, TCP is sent from the File Transfer application in the source host. TCP adds your header information including source and destination port number. Port number is used to separate separate sessions from each other.
Next, the data is sent to the Internet layer. IP protocol adds your header with IP address. Then everything is put in an Ethernet frame, which is sent to the router with the help of a physical address.
The router looks at the physical destination address and sees that this frame itself was addressed. If the checksum contained in the header is correct, the router sends information to the Internet layer and IP protocol.
The router uses the IP destination address and its routing table for further routing processing. In this case, the destination host is on the token ring network.
The router uses the physical address to reach the destination host. Anything sent from the router to the token ring network is taken by the destination host. If the checksum is correct, then this information is transferred to the IP protocol on the Internet layer.
The IP protocol appears in the Datagram and IP destination addresses. If this address is correct then the data is sent to the transport layer above. The TCP protocol looks at the port number in the TCP header and sees that it is FTP data. This data reaches the FTP application on the destination host.
Internet Protocol (IP)
The most important protocol in the TCP / IP family is called Internet Protocol, IP.
The IP protocol defines the structure of data packets, called datagrams.
IP is responsible for logical addresses, which are called IP addresses, and to carry data between the physical and transport layer.
The IP protocol provides a Datagram delivery service between different physical networks where TCP / IP is used. In the TCP / IP network, the router uses the IP protocol to distribute the datagram to the correct destination.
Functions of Internet Protocol (IP)
The main functions of the IP protocol are addresses, routing, and fragmentation.
The IP protocol handles routing with the help of a unique 32-bit IP address. Every host associated with the network has a unique IP address.
Fragmentation is required when two networks want to communicate with each other, but they use different packet sizes. The IP protocol needs to split the packet into smaller datagrams.
The IP protocol is a connectionless protocol, which means that it does not offer a receipt, error checking, and re-transmission. This means that if this physical layer is not controlled by the protocol, then it should be handled by the transport layer.
IP Header
To make the protocol work appropriately, a header is an additional information that should be included in the frame or datagram.
The IP protocols have different functions. It is most important to add logical IP addresses to both source and destination host. This is required for routing.
Other things included in the IP header are:
1. The version number of the IP protocol. The most commonly used version of today is 4, and the next generation IP is called version 6.
2. The IP header also has two fields with length information. IHL, which stands for the length of the internetwork header, specifies how much time a header is and where the data starts from.
3. The total length specifies the number of bytes of both the header and the data.
4. The type of service, TOS, is an area which is usually not used in the IP header.
5. Fragmentation information always starts with a zero, after which two flags are DF, which does not stand for the fragment, and the MF stands for more pieces. If the pieces are then the DF flag will be zero whereas MF will be one.
Fragment offset specifies the necessary information to the destination host to gather pieces in the correct information. It works like this. The destination host has a buffer for different pieces. Fragment offset specifies that the current section starts in the buffer. With the help of total length and IHL, this header is the length, the length of the destination host data segment can be calculated. Destination in this way
The hosts will re-assemble the pieces.
What about the identity field? The objective of the field of identification is to show which pieces are together. The pieces that are simultaneously have identical identification numbers.
6. Live to time, or TTL field is a number that explains how many routers are allowed to pass before dumping the datagram. This is necessary in order to prevent datagram from looping in the network forever. The maximum number that can be set to 255. Each router passing through datagram has reduced this number from 1.
7. Protocol field specifies the protocol on the upper layer, for example, TCP or UDP may be.
8. Header checksum is used to ensure that the contents of the IP header are not corrupted.
9. An IP address is included in two field headers. Another source for the host hosts another destination.
10. Options fields are not commonly used. Sometimes the option is used to specify options through the network
How TCP Work
TCP, which stands for Transmission Control Protocol, is one of two transport protocols in the TCP / IP family. The second is the UDP.
There are two main functions in TCP. Transfer data between the first two hosts in a reliable way. The second task is to distribute data to the right session or the application located on layers above TCP.
1. TCP creates a reliable service on top of Internet Protocol. This is done with the help of three-way handshaking. The source sends a sync signal. The destination sends an approval for that signal and its synchronization signal. The source accepts that signal. The connection is now established and the data can be transferred reliably. Since TCP works in this fashion, it is called a connection-oriented protocol.
2. A port number and the IP address is used to get a unique connection between two hosts. If different sessions are coming from the same host, different port numbers are used to separate these sessions.
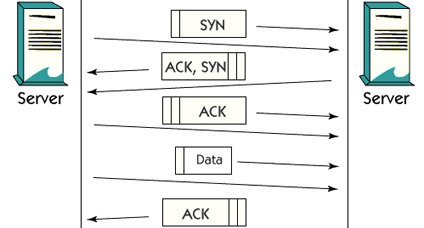
TCP Connection
There is a three-way handshake in a TCP connection before transferring data between two hosts.
The first synchronization flag, called SYN, is sent from the source host to the destination. An ACK stands for acceptance, and a new SEN flag is returned back. It should also be confirmed by the source through the ACK. Now the connection is established and data transfer may start.
All data transferred is sent together with the serial number. This number is used to restore the data in the correct order, but there is also a checksum function, which shows how many bytes of data are transferred. The data transferred should be confirmed with the ACK by the destination host.
TCP Numbering
The synchronization signal sent by the source host contains a synchronization flag SYN, but it also contains a sequence number that provides the destination host with a reference point to access the data.
The destination host sends a signal that has four different items. The first is an ACK flag and the other is a SEN flag. The third item is the sequence number that gives the source host a reference point for the data coming from the destination host. A fourth item is a receipt number which is the sequence number that the source host should use next time. The reason for this is to ensure that communication is appropriate and
Reliable
The source host sends an approval signal that contains three separate items. The first is an ACK flag and the second is the original serial number, increased by 1. A third item is a receipt number which is the sequence number that the destination host should use next time.
Now the source host sends your data with the sequence number. This number has increased by the number of bytes transferred to the previous sequence number. The destination host accepts it by sending a signal that has three separate items. First ACK flag, next sequence number and finally an acknowledgment
Number.
Accept TCP (ACK)
A host that sends information to another host always saves a copy of the data sent.
When a receipt is received then the copy of the data is cleared, but if something goes wrong, then the copy of the data is reproduced.
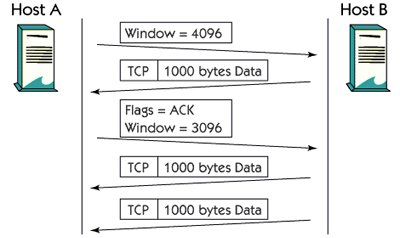
TCP Windows
Curved shapes are used for flow control. This specifies how many additional bytes the destination host is ready to accept. This function is used when the app is not able to handle all the received data on the above layer.
In the photo, Host A sets a buffer of 4096 bytes for incoming packets. Host B sends 1000 bytes to data. A buffer at Host A is full of 1000 bytes and the window size decreases to 3096 bytes.
Many continuous packets can be sent without the need for acceptance. The only important thing is that B does not handle more data than buffer on host A.
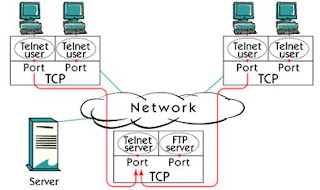
TCP Application Ports
Port numbers are used to separate separate sessions from each other.
There are two types of ports, server ports, and customer ports. Server port is a number between 1 and 1023. The client port is a random number between 1024 and 65535.
For the widely used services, such as Telnet and FTP, these numbers have to be centrally administered. It is regulated in an RFC standard document. This RFC is 1700, whose title is the assigned number. This RFC tells other things as well as the port number assigned to the famous services.
A server can handle multiple sessions at the same time. Identify a unique session between client and server's port number, source and destination host, with the IP address of the client and the server.
For example, many Telnet sessions in the picture are handled by a single host. All sessions are using the same server port number, 23, which is the server port for Telnet. TCP is capable of separating those connections from one another because they all come from different customer ports.
Functions of UDP (User Datagrame Protocol)
TCP is not the only transport protocol in the TCP / IP family. Actually, there are two. The second is the UDP, which is for User Datagram Protocol.
UDP is not capable of handling handshaking. This means that the UDP is a connectionless protocol.
The reliability should be provided by the application rather than the transport protocol.
Like TCP, UDP allows remote machines to contact a service on a certain port, but this connection does not establish. Instead, you can use it to send single packets to the destination service. It is perfect for broadcasting traffic, where all the hosts on the network are addressed to traffic.
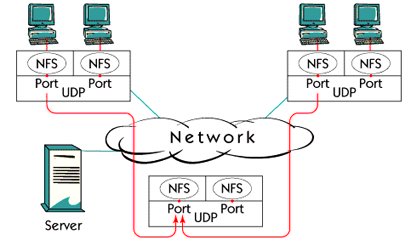
UDP Application Ports
Application port in UDP works in the same way as in TCP. With the IP address of the client and the server, the client and the server's port number identify a unique session between the source and the destination host.
Port number is used to send the correct number of data. There are many types of applications using UDP. Some examples are NFS (Network File System), SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) and DNS (Domain Name Service).
See: How to Google?
See: How to Become a Computer Expert?


.png)























No comments:
Post a Comment