What is Computer Programming?
Computer Characteristics- The computer is used to broadcast, store and manipulate information ie data
Data type:
- Numerical Data
- Character Data
- Graphics Data
- Sound
- In order to process a particular set of data, the computer must be given a suitable set of instructions called Program.
what is the Program
- A computer program is a sequence of instructions (written in a special sequence in the computer-related language) which is executed by a CPU.
- Machine Code or Machine Language
Machine Language Instruction
A computer machine can interpret and execute a set of instructions coded to language instructions.
Operation Code Memory Location
1. 0110 10001110
2. 111 10001111
3. 1000 01110001
- Load from memory location (0110) 10001110 in a CPU register
- Add 10001111 content (0111) to the value of the register
- The result which is in the register is to copy (1000) in the location of memory 01110001.
Problems with Machine Language Coding
- Very cumbersome to work: Hundreds of thousands of locations in more than 100 different machine instruction codes and memory.
- Different types of computers have their own unique instructions set: Operation codes differ from one machine to another
- A machine language program written for one type of computer cannot be played on any other type of computer without significant changes.
- Rewrite the program for different machines.
Note: Computer programs should be written in high-level programming languages which are independent of machine language.
High-Level Language
- One instruction in a high-level language is equivalent to many machine language instructions.
- Simplicity - The instruction set is more compatible with human language.
- Uniformity and portability - A program written for a computer can usually be run on many different computers with little or no change.
- General Purpose Language - C, Pascal, Fortran, and Basic.
- Special Purpose Language - CSMP, SIMAN: Simulation Language - LISP: List processing language, widely used for AI.
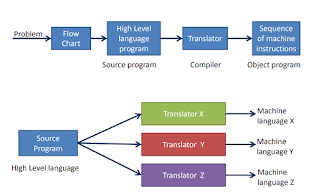
Compilation or Interpretation
- Compiler: - Before executing any instruction, translate the whole program into machine language.
- Interpreter: - The procedure through a program by translating and executing single instructions or small group instructions
- The complainant/interpreter is a computer program in its own right. It accepts a program in the form of input like C in a high-level language and generates a related machine language program as the output.
- A high-level program is called the source program
- The resultant machine language program is called an object program.
- Each computer's fruit has its own compiler or interpreter for a particular high-level language.
Computer Language
Computer Algorithm
- The basic knowledge needed to solve problems using a computer.
- Definition: - A finite sequence of instructions to solve the given problem.
- The instruction should be written invaluable signage, interpreted and executed by a computing machine, which is called computer programming
- Signaling is called a computer programming language.
- Programming Language - Artificial language that can be used to control the behavior of the computer - is defined by the syntactic and semantic rules that describe their structure and meaning respectively.
- Example: Different syntax (languages), but results in the same semantics:
-- x: = x + y; (Pascal)
-- x = x + y; (Initial basic)
-- x = x + y (most basic bids, Fortran)
Developing Algorithms
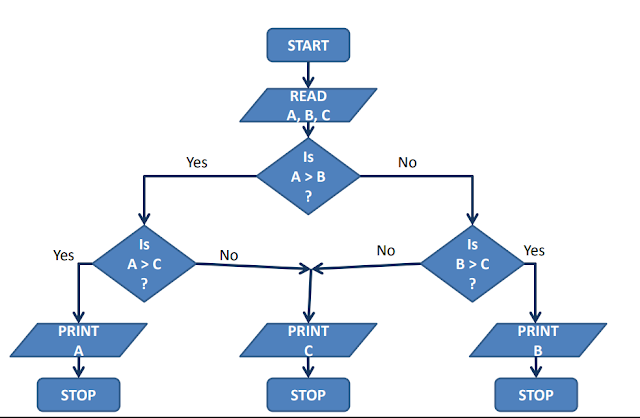
- Flow chart - Graphically shows the sequence in which the instructions are performed in an algorithm.
Pick the largest of three nos
Flow Chart
Convention
- The parallelogram is used to represent the input/output.
- The rectangular is used to indicate any processing operation such as storage and arithmetic.
- The diamond-shaped box is used to test the queries or situations being asked.
- - Round rectangles with rounded ends are used to indicate beginning or endpoints.
- - The circle is used to connect the different parts of the flow chart, which is called the connector.
- - Arrow indicates the direction to be followed in the flow chart.


.png)
















The brilliant and clear manner by which Google is composed is in charge of the important logo we as a whole recall. On second thought, how might you feel if Google was in highly contrasting? Really odd, I assume?
ReplyDeletelogo design service
This is really a nice and informative, containing all information and also has a great impact on the new technology. Thanks for sharing it https://www.computersciencehomeworkhelpers.com
ReplyDeleteThis is confirmation that such innovation can possibly change organizations and altogether increment efficiency.machine learning certification
ReplyDeleteHave doubts on your economics concepts? Expand your knowledge via Economics Assignment Help services and finish your assignment within your due dates.
ReplyDeleteEconomics Homework Help
Economics Assignment