Ethical Hacking Tutorials - Computer Networking
Devices
You Must Be Familiar with the Icons that Represent the most common tools seen in the basic Plans.
What is Topology?
Using these tools, Local Area Network (LAN) can be made. In a LAN, computers can share resources such as hard drives, printer internet connections, and an administrator can control how these resources are shared when a LAN is being designed, any of the following It is also possible to choose Physical Topology:
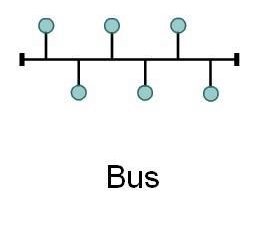
Bus Topology:
In Bus Topology, all computers are connected to the same medium of transmission, and each computer communicates directly with any other.
Ring Topology:
In the Ring Topology configuration, each computer is connected to the following, and the last one, and each computer can communicate directly with only two adjacent computers.
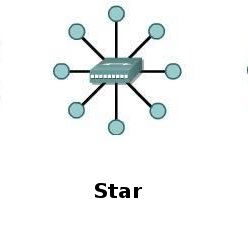
Star Topology:
In Star Topology, none of the computers is directly related to others. Instead, they are connected to a central point and at that central point, the device is responsible for relaying information from computer to computer.
Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol TCP / IP Model
In 1970, TCP / IP was developed by DOD (Defense Department) of the United States and DARPA (Defense Advanced Research Project Agency). TCP / IP was designed as an open standard that any computer can use to connect and exchange simultaneously between them.
TCP / IP model layers
TCP / IP model 4 defines completely independent layers in which it divides the process of communication between the two devices. The layers through which it passes information between the two devices are:
Application Layer
The application layer is the end user's layer. This is the layer which is in charge of translating data from applications into data which can be sent through the network.
The basic functions of this Layer
- Representation
- Coding
- Communication Control
- Application Management
The transport layer installs, maintains and finishes virtual circuits for information transfer. It provides a control mechanism for data flow and allows transmission, and it provides mechanisms to detect errors and improvements.
The information on this layer from the application layer is divided into different segments. The information that comes in the transport layer from the internet layer is sent back to the application layer via ports.
The basic functions of this Layer
- Reliability
- Flow Control
- Correction of False
- Broadcasting
This layer divides the segments of the transport layer into packets and sends packets to the network that is making the Internet. This recipient uses the IP, or Internet Protocol address, to determine the location of the device.
It does not ensure reliability in the connection, because it is already taken care of by the transport layer, but it is responsible for choosing the best route between the original device and the receiver device.
Network Access Layers
This layer is in charge of sending information to both the LAN level and the physical level. It changes all the information that comes from the top layers to the basic information (bits) and directs it to the appropriate location. At this level, the destination of information
Detected by MAC, or Media Access Control, the address of the recipient device.
What is the protocol?
To be able to send information between two devices, both have to speak the same language. This language is called a protocol.
Protocols that appear in the Application Layer of the TCP / IP Model
File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP)
Domain Name Service (DNS)
Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTTP)
The protocol of Transport Layer
Transport Control Protocol (TCP)
User Datagram Protocol (UDP)
Internet Layer Protocol A
Internet Protocol (IP)
The protocol is often used in the network access layer
Ethernet
Application layer protocol
FTP or File Transfer Protocol is used to transmit files between two devices. It uses TCP to create virtual connections for information control, then creates another connection to use for the distribution of data. The most used ports are 20 and 21.
HTTP or Hypertext Transfer Protocol is used to translate the information into web pages. This information is distributed in the way it is used for electronic mail. The port most used is 80.
SMTP or Simple Mail Transfer Protocol is a mail service that is based on the FTP model. It transmits the electronic system between two systems and provides notifications of incoming mail. The most used port is 25.
The DNS or Domain Name Service provides a way to associate a domain name with an IP address. The most used port is 53.
TFTP or Trivial File Transfer Protocols have similar functions to FTP but instead of TCP, they use UDP. This gives it more speed but gives less safety and reliability. The most used port is 69.
Transport layer protocol
Two Protocols can be used by Transport Protocol to distribute information blocks.
TCP or Transmission Control Protocol establishes a logical connection between the final points of the network. It synchronizes and regulates traffic which is known as "Three-Way Handshake". In "Three-Way Handshake", the original device sends an initial packet called an SYN to the receiving device. The recipient device sends a receipt packet, which is called an SYN / ACK.
The original device then sends a packet called an ACK, which is the acceptance of receipt. At this point, both the original device and the recipient device have installed that there is a connection between the two and the two are ready to send and receive data from each other.
The UDP or User Datagram Protocol is a transport protocol that is not based on connections. In this case, the original equipment receiver sends packets without warning to the device without expecting these packets.
It is then up to the recipient device to determine whether the packet will be accepted or not. As a result, the UDP is faster than TCP, but can not guarantee that a packet will be accepted.
Internet Layer Protocol
IP or Internet Protocol acts as a universal protocol to allow any computer to communicate through any network at any time. Like UDP, this connection is unrelated, because it does not establish a connection with a remote computer. Instead, it is known as a best-effort service, in which it will be possible to ensure that it works correctly, but its reliability is not guaranteed.
The Internet Protocol determines the format of packet headers, including the IP address of both the original and the recipient devices.
A domain name is the web address that you typically type into a web browser. That name identifies one or more IP addresses. For example, the domain name microsoft.com represents nearly a dozen IP addresses. The domain names in the URL are used to identify specific web pages.
For example, in the URL http://www.thehacktech.in the domain name is thehacktech.in.
Each domain name contains a suffix that indicates which top-level domain it is (TLD). There is only a limited number of such domains. for example:
.gov - Government Agencies
.edu - Educational Institutions
.org - Organization
.com - Commercial Business
Since the Internet is based on IP address, not a domain name, every web server requires a Domain Name System (DNS) server so that domain names can be translated into an IP address.
IP addresses are identifiers that are used to differentiate between computers connected to the network and other devices. Each device should have a different IP address so that there is no problem of wrong identification within the network.
There are 32 bits in the IP address, which are divided into Four 8-bit Octets, which are different from the points. The part of the IP address identifies the network, and the remaining IP addresses identify different computers on the network.
There are both Public IP Addresses and Private IP Addresses. Private IP addresses are used by private networks, which have no connection to the external networks. The IP address should not be duplicated within that network, in any personal network, but computers on two different computers - but there may be Duplicated IP addresses in the unwanted private network.
The IP addresses as defined by the AINA, Internet Assigned Number Authority, are available as being available for the private network:
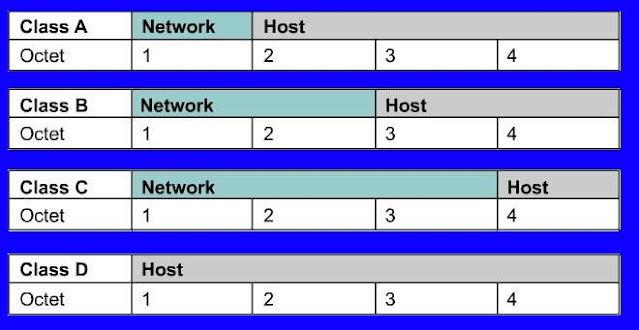
IP addresses are divided into classes, on the basis of which part of the address is used to identify the network and which part is used to identify the personal computer.
Depending on the size allocated to each part, more devices within the network will be allowed, or more networks will be allowed. The current classes.
Class A: The first bit is always zero, so the squares contain addresses between 0.0.0.0 And 126.255.255.255. Note: Address of 127.x.x.x is reserved for services Loopback or localhost
Class B: The first two bits of the first octet are '10', hence the class contains the addresses Between 128.0.0.0 and 19.1.255.255.255
Class C: The first three bits of the first octet are '110', so this class contains Addresses between 19.0.0.0 and 223.255.255.255.
Class D: The first four bits of the first octet are '1110', so this class contains Addresses between 224.0.0.0 and 23 9.255.255.255. These addresses are reserved Group Multicast implementation.
The remaining addresses are used for use or for potential future Allocation
TCP and UDP use ports to exchange information with both applications. A port is an extension of an address, similar to adding an apartment or room number to a street or address. A letter with a street address will arrive at the right apartment building, but without the apartment number, it will not be given to the right recipient. The ports work in the same way.
A packet can be delivered to the correct IP address, but without the related port, there is no way to determine which app should work on the packet.
Once defining ports, it is possible for different types of information that are sent to an IP address so that appropriate applications can be sent.
Using ports, one service running on a remote computer can determine what types of information the local client is requesting, can determine the protocol needed to send that information, and many different customers Together they can maintain communication together.
For example, if a local computer attempts to connect to the website www.thehacktech.in whose IP address is 62.80.122.203, with the webserver running on port 80, remote computer using the local computer socket address Will connect to:
62.80.122.203:80
In order to maintain standards of standardization among the most used ports, IANA has established that ports ranging from 0 to 1024 should be used for general services.
Remaining Port - through 65535 - is used for dynamic allocation or special Services.
The most used Ports as assigned by IANA are listed here
0 - - - Reserved
1-4 - - - Unassigned
5 - rje - Remote Job Entry
7 - echo - Echo
9 - discard - Discard
11 - systat - Active Users
13 - daytime - Daytime
15 - netstat - Who is Up or NETSTAT
17 - qotd - Quote of the Day
19 - chargen - Character Generator
20 - ftp-data - File Transfer
21 - ftp - File Transfer Protocol
22 - ssh - SSH Remote Login Protocol
23 - telnet - Telnet
25 - smtp - Simple Mail Transfer
37 - time - Time
39 - rlp - Resource Location Protocol
42 - nameserver - Host Name Server
43 - nicname - Who Is
53 - domain - Domain Name Server
67 - bootps - Bootstrap Protocol Server
68 - bootpc - Bootstrap Protocol Client
69 - tftp - Trivial File Transfer
70 - gopher - Gopher
75 - - - Any private dial out service
77 - - - Any private RJE service
79 - finger - Finger
80 - www-http - World Wide Web HTTP
95 - supdup - SUPDUP
101 - hostname - NIC Host Name Server
102 - iso-tsap - ISO-TSAP Class 0
110 - pop3 - Post Office Protocol - Version 3
113 - auth - Authentication Service
117 - uucp-path - UUCP Path Service
119 - nntp - Network News Transfer Protocol
123 - ntp - Network Time Protocol
137 - netbios-ns - NETBIOS Name Service
138 - netbios-dgm - NETBIOS Datagram Service
139 - netbios-ssn - NETBIOS Session Service
140-159 - - - Unassigned
160-223 - - - Reserved
Internet Layer Protocol
IP or Internet Protocol acts as a universal protocol to allow any computer to communicate through any network at any time. Like UDP, this connection is unrelated, because it does not establish a connection with a remote computer. Instead, it is known as a best-effort service, in which it will be possible to ensure that it works correctly, but its reliability is not guaranteed.
The Internet Protocol determines the format of packet headers, including the IP address of both the original and the recipient devices.
What is IP address?
A domain name is the web address that you typically type into a web browser. That name identifies one or more IP addresses. For example, the domain name microsoft.com represents nearly a dozen IP addresses. The domain names in the URL are used to identify specific web pages.
For example, in the URL http://www.thehacktech.in the domain name is thehacktech.in.
Each domain name contains a suffix that indicates which top-level domain it is (TLD). There is only a limited number of such domains. for example:
.gov - Government Agencies
.edu - Educational Institutions
.org - Organization
.com - Commercial Business
Since the Internet is based on IP address, not a domain name, every web server requires a Domain Name System (DNS) server so that domain names can be translated into an IP address.
IP addresses are identifiers that are used to differentiate between computers connected to the network and other devices. Each device should have a different IP address so that there is no problem of wrong identification within the network.
There are 32 bits in the IP address, which are divided into Four 8-bit Octets, which are different from the points. The part of the IP address identifies the network, and the remaining IP addresses identify different computers on the network.
There are both Public IP Addresses and Private IP Addresses. Private IP addresses are used by private networks, which have no connection to the external networks. The IP address should not be duplicated within that network, in any personal network, but computers on two different computers - but there may be Duplicated IP addresses in the unwanted private network.
The IP addresses as defined by the AINA, Internet Assigned Number Authority, are available as being available for the private network:
10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255
172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255
192.168.0.0 to 2.168.255.255
IP addresses are divided into classes, on the basis of which part of the address is used to identify the network and which part is used to identify the personal computer.
Depending on the size allocated to each part, more devices within the network will be allowed, or more networks will be allowed. The current classes.
Class A: The first bit is always zero, so the squares contain addresses between 0.0.0.0 And 126.255.255.255. Note: Address of 127.x.x.x is reserved for services Loopback or localhost
Class B: The first two bits of the first octet are '10', hence the class contains the addresses Between 128.0.0.0 and 19.1.255.255.255
Class C: The first three bits of the first octet are '110', so this class contains Addresses between 19.0.0.0 and 223.255.255.255.
Class D: The first four bits of the first octet are '1110', so this class contains Addresses between 224.0.0.0 and 23 9.255.255.255. These addresses are reserved Group Multicast implementation.
The remaining addresses are used for use or for potential future Allocation
What is Port ?
TCP and UDP use ports to exchange information with both applications. A port is an extension of an address, similar to adding an apartment or room number to a street or address. A letter with a street address will arrive at the right apartment building, but without the apartment number, it will not be given to the right recipient. The ports work in the same way.
A packet can be delivered to the correct IP address, but without the related port, there is no way to determine which app should work on the packet.
Once defining ports, it is possible for different types of information that are sent to an IP address so that appropriate applications can be sent.
Using ports, one service running on a remote computer can determine what types of information the local client is requesting, can determine the protocol needed to send that information, and many different customers Together they can maintain communication together.
For example, if a local computer attempts to connect to the website www.thehacktech.in whose IP address is 62.80.122.203, with the webserver running on port 80, remote computer using the local computer socket address Will connect to:
62.80.122.203:80
In order to maintain standards of standardization among the most used ports, IANA has established that ports ranging from 0 to 1024 should be used for general services.
Remaining Port - through 65535 - is used for dynamic allocation or special Services.
The most used Ports as assigned by IANA are listed here
0 - - - Reserved
1-4 - - - Unassigned
5 - rje - Remote Job Entry
7 - echo - Echo
9 - discard - Discard
11 - systat - Active Users
13 - daytime - Daytime
15 - netstat - Who is Up or NETSTAT
17 - qotd - Quote of the Day
19 - chargen - Character Generator
20 - ftp-data - File Transfer
21 - ftp - File Transfer Protocol
22 - ssh - SSH Remote Login Protocol
23 - telnet - Telnet
25 - smtp - Simple Mail Transfer
37 - time - Time
39 - rlp - Resource Location Protocol
42 - nameserver - Host Name Server
43 - nicname - Who Is
53 - domain - Domain Name Server
67 - bootps - Bootstrap Protocol Server
68 - bootpc - Bootstrap Protocol Client
69 - tftp - Trivial File Transfer
70 - gopher - Gopher
75 - - - Any private dial out service
77 - - - Any private RJE service
79 - finger - Finger
80 - www-http - World Wide Web HTTP
95 - supdup - SUPDUP
101 - hostname - NIC Host Name Server
102 - iso-tsap - ISO-TSAP Class 0
110 - pop3 - Post Office Protocol - Version 3
113 - auth - Authentication Service
117 - uucp-path - UUCP Path Service
119 - nntp - Network News Transfer Protocol
123 - ntp - Network Time Protocol
137 - netbios-ns - NETBIOS Name Service
138 - netbios-dgm - NETBIOS Datagram Service
139 - netbios-ssn - NETBIOS Session Service
140-159 - - - Unassigned
160-223 - - - Reserved


.png)

















No comments:
Post a Comment